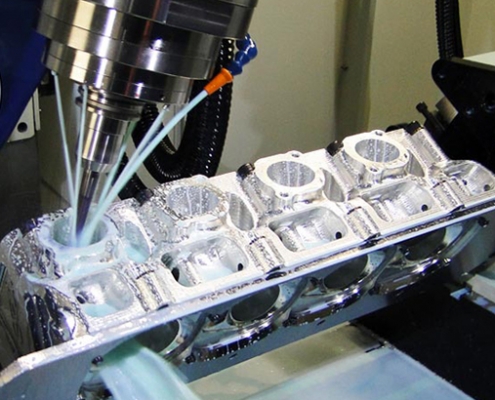
What are Some Examples of CNC Machined Parts?
Ever wondered how intricate parts in everyday objects and advanced machinery are made? Traditional manufacturing methods often lack the precision and efficiency needed for complex designs. CNC machining steps in to deliver high-quality, custom-made parts across various industries.
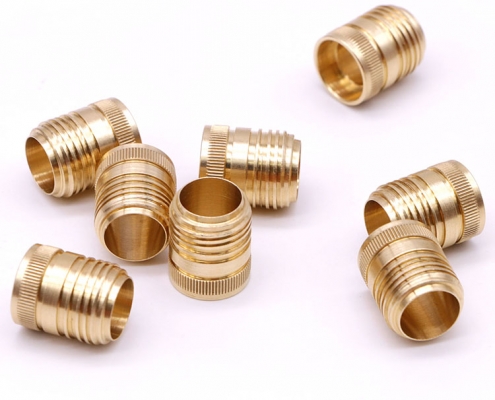
CNC machining produces diverse parts, from simple brackets to complex engine components. Examples include gears, medical implants, aerospace components, automotive parts, and electronic enclosures, showcasing its versatility across industries requiring precision and customization.
Let’s delve deeper into what CNC machining entails, the various types of CNC machining processes, materials used, and specific examples of CNC machined parts across different sectors.
What are CNC Machined Parts?
CNC machined parts refer to components that have been produced using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology, which automates the machine tools required for manufacturing. In the parts CNC machining process, pre-programmed computer software controls the movement of machinery and tools to create precise parts and components. CNC machining is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process, enabling the production of CNC machine products with high accuracy and repeatability.
From intricate prototypes to high-volume production, CNC machined parts are essential across a wide range of industries, offering superior quality and consistency. The ability to customize designs and meet exact specifications makes CNC machined parts a go-to solution for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
What is CNC Manufacturing?
CNC manufacturing is a subtractive process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This automated process allows for precise cutting, drilling, and shaping of various materials like metal, plastic, and wood to create intricate parts with high accuracy and repeatability. Whether producing CNC milled parts or complex machined parts, this technology ensures the highest level of precision.
CNC machining offers several advantages over manual machining, including increased speed, precision, consistency, and the ability to create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve manually. With precision CNC machined parts, manufacturers can create CNC parts that meet exact specifications for various applications. Parts of CNC machines such as motors, spindles, and controllers, along with CNC machine components, are integral to this efficient process, driving the production of high-quality CNC machining parts with unmatched accuracy.
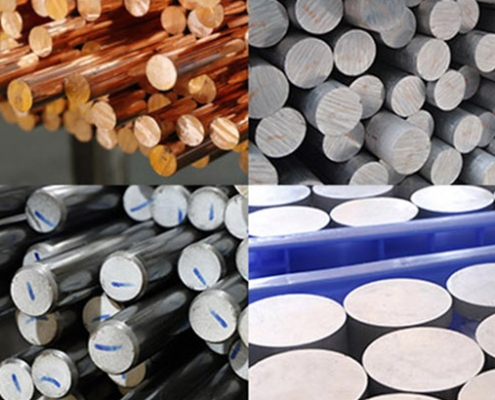
Common Types of Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining’s versatility extends to its ability to work with a wide range of materials, each offering specific properties and advantages for different applications. Metals like aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium are commonly used, along with plastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, as well as wood, composites, and even foam in certain applications.
- Aluminum is lightweight, strong, and easy to machine, making it suitable for parts requiring a good strength-to-weight ratio.
- Steel offers high strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Brass is known for its machinability and corrosion resistance, often used in decorative and plumbing parts.
- Titanium, a strong and lightweight metal with excellent biocompatibility, is commonly used in medical implants and aerospace components.
How to Choose the Right Material for Your CNC Machined Parts?
Selecting the appropriate material for CNC machining is crucial for ensuring the part’s functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Factors to consider include the part’s intended use, required strength and stiffness, environmental conditions, budget constraints, and aesthetic considerations.
When making a decision, you should consider the material’s mechanical properties like strength, stiffness, and hardness. Its machinability, which refers to the ease of cutting and shaping, is also important.
Additionally, you need to think about the material’s corrosion resistance, thermal properties such as heat resistance and conductivity, and, of course, its cost. Often, there are trade-offs to be made, as a material with high strength might come at a higher price or be more challenging to machine. For instance, stainless steel is chosen for marine applications due to its corrosion resistance, while aluminum is preferred for aerospace components because of its lightweight properties.
Five Most Common Types of Precision CNC Machining
CNC machining encompasses various specialized techniques to achieve specific results and cater to diverse material and design requirements. Common types include CNC milling, turning, routing, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and laser cutting, each offering unique capabilities for shaping and finishing parts. Here’s a detailed look at the five most common types of precision CNC machining:
1. CNC Milling
CNC milling employs rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece, effectively creating complex 3D shapes. This versatile technique can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. CNC milling is capable of fabricating intricate geometries, slots, holes, and surface contours, and is commonly used for manufacturing housings, brackets, complex components for machinery, and prototypes.
2. CNC Turning
CNC turning involves rotating the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material, making it particularly suited for producing cylindrical and symmetrical shapes. This method allows for precise control over dimensions and surface finish, ideal for parts with varying lengths and diameters. CNC turning is widely used to create shafts, bushings, fittings, and components for the automotive and aerospace industries.
3. CNC Routing
CNC routing utilizes a high-speed rotating tool to cut and shape materials such as wood, plastics, and composites. This technique is especially effective for creating detailed profiles, signs, and intricate patterns. CNC routers can handle sheet materials and larger workpieces, making them a popular choice in woodworking, cabinetry, signage production, and the manufacturing of templates and fixtures.
4. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM uses controlled electrical discharges to erode material, allowing for the precise shaping of hard metals and intricate features. This method is excellent for creating complex geometries, including internal features and fine details that may be difficult to achieve using traditional cutting methods. EDM is commonly used in die-making, mold fabrication, and aerospace components where precision machining of hard materials is critical.
5. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to cut and engrave materials with high precision. This non-contact method produces clean edges and can achieve intricate designs with tight tolerances. It works well on various materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Laser cutting is widely used for cutting sheet metal, signage, custom designs, decorative applications, and prototyping.
Examples of CNC Machined Parts
CNC machining is widely used across industries to produce precise, durable, and high-quality CNC machined parts. From complex CNC components to intricate machining parts for the chemical industry, the versatility of CNC machining is unmatched. Below are notable examples of CNC scenarios and their applications in various sectors:
CNC Machined Parts in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on CNC machining to produce a diverse range of precision machining parts to ensure optimal vehicle performance, safety, and aesthetics. Engine components such as pistons, cylinder heads, and crankshafts undergo precise machining of special parts for high performance. Additionally, exterior parts like door handles and grilles achieve intricate designs through CNC machining.
Aluminum alloys are commonly used for engine blocks and cylinder heads due to their lightweight and good thermal conductivity. Steel is used for crankshafts and connecting rods for its high strength and durability. Precision in automotive CNC machining is critical for ensuring proper engine performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
CNC Machining in Medical Device Manufacturing
CNC machined parts for medical devices demand high precision and biocompatibility, making CNC machining an ideal method for producing implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. CNC machining creates intricate turned mechanical parts like hip implants, bone plates, and surgical tools with tight tolerances and smooth finishes, crucial for patient safety.
Titanium and stainless steel are preferred materials for medical implants due to their biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength. CNC machining ensures the precise dimensions and surface finish required for implants to integrate properly with the human body. Sterilization and rigorous quality control are essential in medical CNC machining to maintain product integrity and patient safety.
Aerospace Applications of CNC Machined Parts
The aerospace industry requires lightweight yet incredibly strong and precise components. CNC machining plays a vital role in crafting machined components for chemical equipment, turbine blades, fuel injectors, and structural parts for aircraft, spacecraft, and satellites. CNC machining ensures the reliability and performance of aerospace systems.
Materials like aluminum alloys, titanium, and high-strength composites are commonly used in aerospace applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures. Rigorous quality control and adherence to aerospace standards are paramount to ensure the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft components.
CNC Machining for Industrial Equipment
Industrial equipment relies on durable and precisely manufactured parts to withstand demanding operating conditions. CNC machining products are essential in automation systems, robotics, and heavy machinery. Gears, shafts, bearings, and robotic arms are precisely machined to ensure smooth operation and longevity in industrial settings.
Steel alloys and hardened plastics are commonly used in industrial CNC machining for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. CNC machining enables the creation of machined parts with complex geometries and precise tolerances required for the most demanding industrial applications.
CNC Machined Parts in Electronics
From smartphones to laptops, CNC machining plays a significant role in creating the intricate components of electronic devices. CNC machining produces parts like enclosures, heat sinks, connectors, and internal components for consumer electronics, ensuring functionality and aesthetics.
Materials such as aluminum, magnesium alloys, and plastics are commonly used in electronics CNC machining. Aluminum offers a good balance of strength, lightweight, and heat dissipation. Magnesium alloys provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios, while plastics offer design flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Precision and surface finish are crucial in CNC machined products to ensure proper fit, function, and aesthetic appeal.
CNC Machining for Optical Components and Instruments
CNC machining is essential for creating optical components with extremely precise surfaces and tight tolerances. CNC machines are used to craft lenses for cameras, telescopes, and microscopes, ensuring optimal optical performance. CNC technology is also employed to create precise housings for laser systems and other optical devices.
The Role of CNC Machining in Prototyping and Customization
CNC machining enables the creation of functional prototypes from various materials, allowing engineers to test form, fit, and function before committing to large-scale production. Custom tooling allows for the production of highly specialized parts that may not be available through standard manufacturing processes. CNC machining plays a significant role in low-volume manufacturing and niche applications where customization and rapid prototyping are essential.
In sum, From machining examples in the automotive and medical sectors to precision CNC components in aerospace, CNC machining is indispensable across industries for producing highly precise, durable, and complex machined components. The technology ensures accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency in creating parts that meet the stringent requirements of various applications. Whether producing CNC parts, CNC machining products, or custom CNC machined parts, this versatile process enables the creation of intricate designs and high-quality components tailored to specific industry needs.
In Conclusion
CNC machining is a versatile and essential manufacturing process used to create a wide range of precise and intricate parts across numerous industries. By understanding the different types of CNC machining, materials used, and applications, you can appreciate its impact on modern technology and everyday life.
Start Your CNC Machining Parts Project
Start your CNC machining parts project with VMT, a trusted manufacturer backed by 14 years of industry-leading expertise. Our advanced facility boasts 100 imported machines, enabling rapid prototyping with samples delivered in just 3 days and small-batch orders ready in 7.
In addition, our rigorous 12-step inspection process ensures a batch processing yield rate of up to 98%, thanks to our team of 6 seasoned technicians with over 20 years each in process optimization. Partner with us for precision, speed, and unparalleled quality in every aspect of your CNC machining needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About CNC Machined Parts
What Is Machining a Part for a Product an Example Of?
Machining a part for a product is an example of a subtractive manufacturing process. This involves removing material from a workpiece using tools like lathes, mills, or drills to create precise shapes and dimensions. It is commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics for creating high-precision components.
What Parts Can You Make with a CNC Machine?
A CNC machine can produce a wide variety of parts, including gears, brackets, housings, medical implants, and engine components. It excels at creating intricate designs, prototypes, and custom parts for industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and manufacturing. The versatility of CNC machines allows them to work with metals, plastics, and composites.
What Is the Difference Between Fabricated and Machined?
The key difference lies in the process. Fabricated parts are created by joining or assembling materials, often through welding, bending, or cutting. In contrast, machined parts are produced by precisely removing material from a workpiece using tools like CNC machines. Fabrication is ideal for large, simple structures, while machining is suited for detailed, precise components.