Laser Etching vs Engraving: A Difference Guide
In manufacturing and customization industries, laser technology plays a vital role in creating precise, permanent markings. Among the most popular methods are laser etching and laser engraving, which are both widely used in CNC machining, metal part marking, and custom product detailing.
Many people confuse etching vs engraving, not realizing they differ in depth, durability, process, and cost. Using the wrong method can affect product lifespan, appearance, and function, especially in industries where tolerance and surface integrity matter.
This article explores what is laser etching, what is laser engraving, their importance, detailed differences, and how to choose the right process. Whether you’re searching for a laser engraving service or a laser engraver for metal, understanding these distinctions will help you make the best decision.
What is Laser Etching?
Laser etching is a subset of laser marking where a laser beam alters the surface of a material by melting it to form raised marks. The laser changes the reflectivity and texture of the material, typically penetrating less than 0.001 inches.
Laser etching is faster than engraving and ideal for thin surfaces or parts that can’t tolerate deep cuts. It’s used in laser etched clothing, laser etched tumblers, and laser etching shoes, where cosmetic markings matter more than depth.
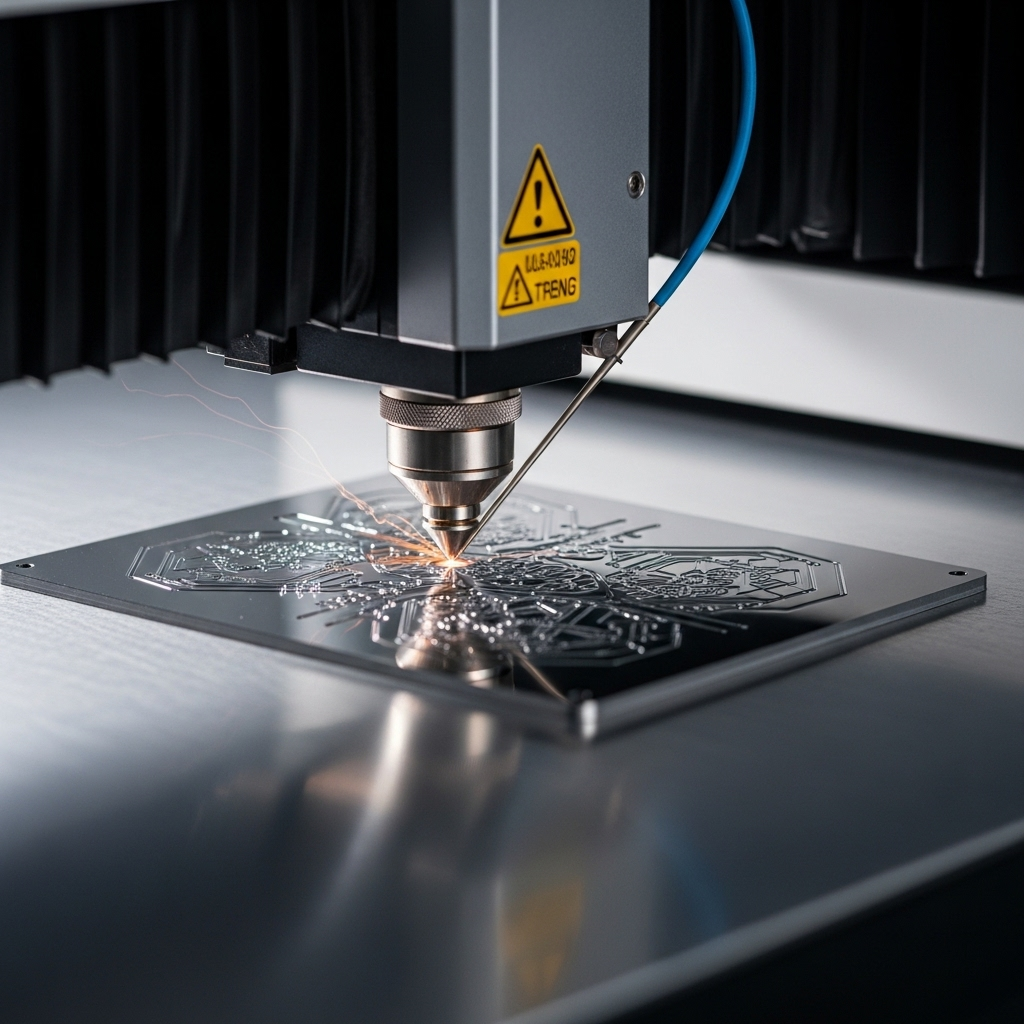

What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving removes material from the surface using a focused laser beam, creating deep cavities that are permanent and resistant to wear. Unlike etching laser, engraving digs deeper, often up to 0.005 inches or more.
This process is best for applications requiring high durability, such as industrial tools, automotive parts, and military equipment. Laser engravers near me often offer engraving for products that undergo friction, corrosion, or environmental exposure.
Why Are Laser Etching and Engraving Important?
Laser etching and engraving are essential techniques for marking materials without causing damage or wear. They help track and identify parts in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
These methods are also perfect for adding a personal touch to items like jewelry, gifts, and gadgets. By providing precise and durable results, laser etching and engraving make it easy to create custom designs or meet strict industry requirements.
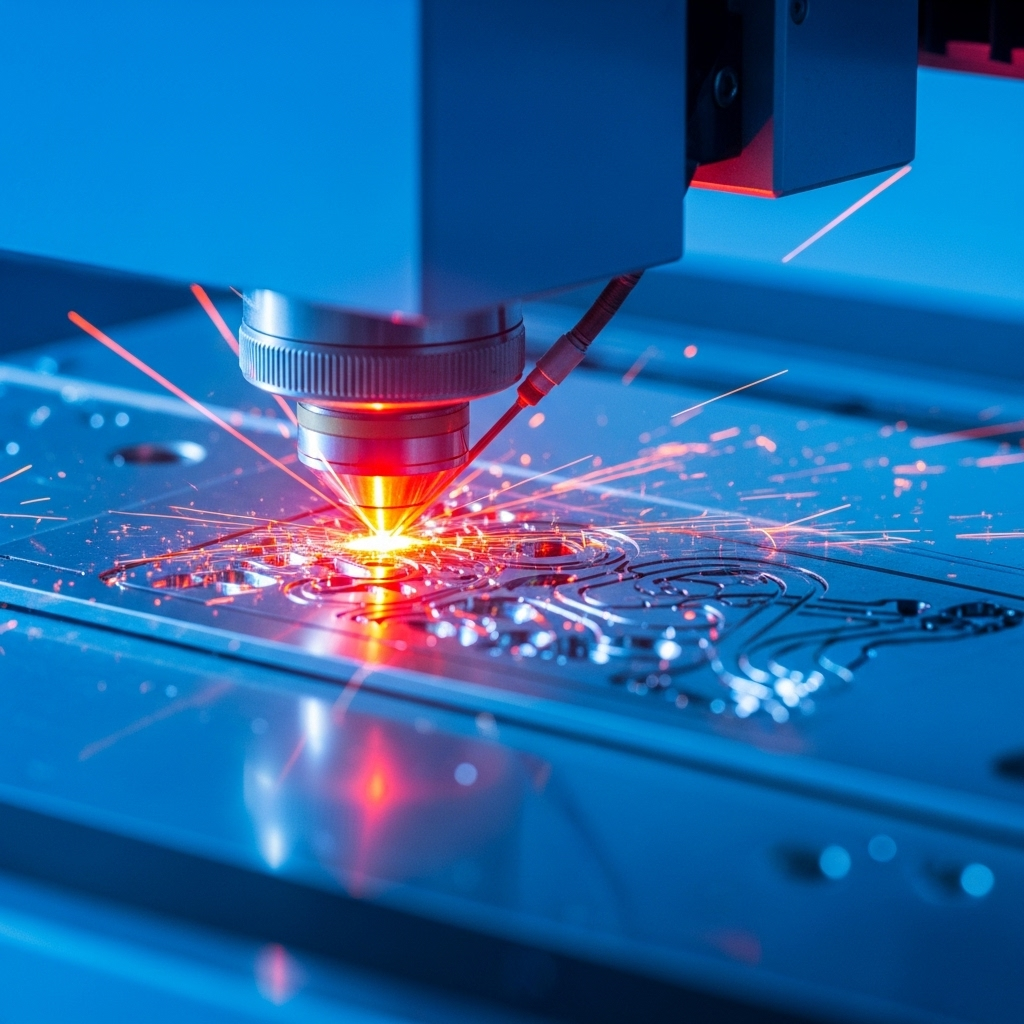

Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Compare Their Differences
Understanding the difference between engraving and etching is essential in CNC machining, product customization, and high-precision manufacturing. Below is a deep comparison of both techniques across multiple dimensions.
1. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Processing Time
Laser etching is significantly faster than engraving because it alters only the surface of the material. It typically requires less dwell time and lower laser power, making it ideal for high-speed production lines where throughput is critical.
Laser engraving requires the laser to cut deeper into the material. This involves longer processing cycles and multiple passes, especially on harder metals. The increased time results in stronger, more durable marks, but at the cost of speed.
2. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Machine Wear and Tear
Since laser etching uses lower power and quicker pulses, it results in minimal strain on the laser optics and focusing lenses. The overall wear on machinery remains low, preserving the lifespan of the equipment and reducing maintenance frequency.
In contrast, laser engraving exerts more stress on the system. It operates under higher thermal loads, and longer exposure leads to quicker degradation of components, especially when engraving harder metals like stainless steel or titanium.
3. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Energy Consumption
Because laser etching is shallower and faster, it consumes much less energy. It’s a power-efficient solution for marking large quantities of parts with barcodes, logos, or identification numbers.
Laser engraving uses more energy to penetrate deeper into the material. Its higher wattage requirements and extended run times increase electricity consumption, making it a less energy-efficient process overall.
4. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Cutting Depth
Etching alters only the top microns of the material surface—typically less than 0.001 inches. It creates a visible mark without structurally weakening the part, which is ideal for components where strength must remain uncompromised.
Engraving removes more material—often from 0.003 to 0.005 inches deep, or more depending on the requirement. This depth gives it durability, making engraved marks ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments or frequent handling.
5. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Precision
Both processes offer high precision, but laser etching excels in extremely detailed surface marks. It is perfect for QR codes, fine text, and decorative patterns, particularly on thin metals or coated surfaces.
Laser engraving also delivers precision but is better suited for applications requiring readable, permanent detail on structural parts. It can be applied on uneven or curved surfaces while maintaining clarity.
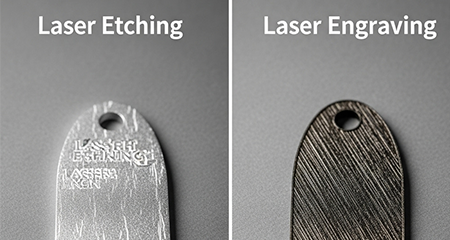
6. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Surface Finish Difference
Etching produces a smooth, high-contrast surface mark. Since it affects only the outer layer, the result is a clean and often shiny or frosted appearance that can enhance product branding or part identification.
Engraving results in a recessed, rougher texture. It may require post-processing like polishing, depending on the desired finish. The engraved area is more pronounced, offering tactile feedback and high durability.
7. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Appearance
The marks created by laser etching are subtle and cosmetic. They blend seamlessly with the material’s natural finish and are ideal for branding, aesthetics, or traceability on parts with strict appearance requirements.
Laser engraving provides a bold, visible mark that can often be felt by touch. It’s preferred in industrial environments where visibility, contrast, and permanence are more important than cosmetic appeal.
8. Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: Cost Differences
Since laser etching uses less energy and requires shorter cycle times, the operational cost is generally lower. It’s often the preferred choice for budget-conscious projects that still demand professional results.
Laser engraving tends to be more expensive due to higher power usage, slower production rates, and more frequent equipment maintenance. However, the durability and quality of the results can justify the investment in long-term applications
Summary Table: Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving
| Feature | Laser Etching | Laser Engraving |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Faster, ideal for high-volume applications | Slower due to deeper material removal |
| Machine Wear | Minimal wear, lower maintenance | Higher wear, frequent maintenance on optical and mechanical parts |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy usage due to shallow marking | Higher power consumption and longer processing time |
| Cutting Depth | Very shallow (microns) | Deep cuts (up to several millimeters) |
| Precision | High precision for fine, cosmetic detailing | High precision for durable, readable marks |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, clean, with high contrast | Rougher, may need post-polishing |
| Appearance | Subtle and aesthetic | Bold, tactile, industrial-grade finish |
| Cost Differences | Lower operational and equipment costs | Higher cost due to energy use and machine stress |
Which One is Right for Your CNC Project?
Choosing between laser etching and engraving depends on your specific needs. If you want quick results with detailed designs and minimal wear on materials like metal or plastic, laser etching works best.
For projects that require deep and permanent markings built to withstand tough conditions, such as those in aerospace or medical applications, laser engraving is the ideal choice.
In Conclusion
The main differences between laser etching and laser engraving are depth, durability, and application. Etching and engraving should be done with caution, especially in CNC part marking, as surface accuracy can affect performance.
If you are looking for laser engraving services or laser engraving companies near you, VMT is a great place to find custom laser etching and engraving services tailored to your needs. We also offer surface finishing services such as anodizing, coating, polishing, grinding, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions About Laser Etching and Laser Engraving
Is Laser Etching Different from Laser Engraving?
Yes, laser etching alters only the surface by melting it, creating shallow marks, while laser engraving removes material to create deeper, permanent impressions. Etching is faster and better for light markings, whereas engraving offers more durability and depth.
How to Remove Laser Etching from Metal?
To remove laser etching from metal, you can use abrasive polishing, sanding, or grinding tools. For light etching, buffing with a rotary tool and polishing compound may be enough. Deeper removal may require resurfacing the metal.
How to Laser Etch Acrylic?
Use a CO2 laser with low power and high speed. Place a masking film on the acrylic surface for cleaner results. Set the laser to raster mode and focus on the surface to achieve a frosted, white mark without burning.
How to Laser Engrave Glass?
Use a CO2 laser with low power and high resolution. Apply masking tape or a wet paper layer on the glass to reduce cracking. Set the laser to engrave gently in multiple passes for best results with minimal chipping.
How to Reverse a Depth Design for Laser Engraving?
To reverse a depth design, invert the grayscale image or vector fill so that the laser engraves less where it normally would engrave more. This creates raised effects around your design, commonly used for molds or stamps.
How to Use a Laser Engraver?
First, set up your laser engraving machine with the correct material. Upload your design using compatible software. Adjust power, speed, and focus based on the material. Secure the workpiece, then start engraving while monitoring the process for safety.



