8 Types of Aluminum Finishes That Will Enhance Your CNC Parts
Are you worried about your aluminum CNC parts getting scratched and losing their aesthetic appeal? Are you tired of looking at dull, uninspired surfaces on your precision components? A subpar finish can compromise both the look and durability of your product.
Choosing the right finish is crucial for protecting your aluminum CNC parts and improving their appearance. The most common types of aluminum finishes include anodizing, powder coating, bead blasting, brushing, and polishing, each offering unique benefits for aesthetics, durability, and corrosion resistance to meet specific application requirements.
Let’s dive into the details and find the perfect finish for your next project.
Understanding Aluminum Finishing: Why It Matters?
Surface finishes play a crucial role in determining how a CNC machined aluminum part performs in real-world applications. Finishing is more than just a final step; it’s a critical process that determines the performance and longevity of a part. Finishes shield against corrosion and wear, which is especially important for parts exposed to harsh environments.
A proper finish can also enhance visual appeal, creating a custom, high-end look that stands out in the market. Beyond aesthetics, finishes can improve a part’s functionality by altering properties like electrical conductivity, surface hardness, or friction. Ultimately, selecting the right finish is a cost-effective decision that balances performance with budget.
Type 1: Anodizing Anodised Aluminium Finish
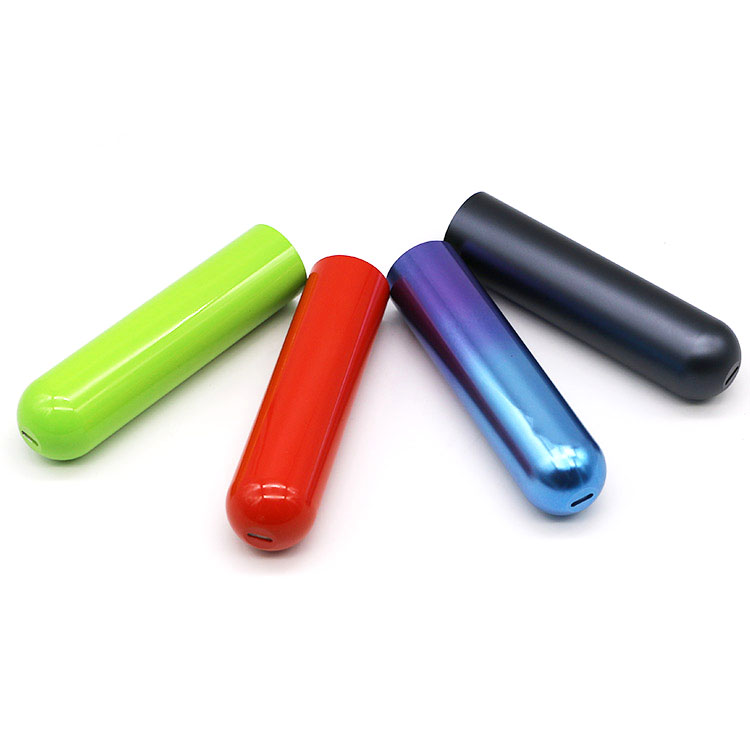
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, porous oxide layer. This types of aluminum surface finishes creates a hard, corrosion-resistant surface that is more durable than raw aluminum. The process allows for a wide range of colors, from vibrant hues to a subtle matte finish, depending on the dye used.
Anodizing is classified into different types. Type II, or standard anodizing, is a general-purpose, durable finish. Type III, or hardcoat anodizing, offers maximum durability, wear resistance, and thickness, making it ideal for harsh environments. Anodizing is a popular choice for consumer electronics, architectural components, and military equipment. This method is especially beneficial for parts exposed to harsh environments or requiring a decorative yet functional layer.
Type 2: Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder and then curing it with heat to create a hard protective layer. Powder coating is ideal for parts that need both a visually appealing appearance and robust protection. Compared to other types of finishes for aluminum, it provides excellent color retention and environmental resistance.
Powder coating provides a vast selection of colors and textures, allowing for a high degree of customization. The process involves surface preparation, an electrostatic application of the powder, and a final curing in an oven. It’s often used on automotive parts, industrial equipment, and outdoor furniture where a tough, long-lasting finish is essential.
Type 3: Bead Blasting
Bead blasting is a surface treatment process that involves forcefully propelling fine abrasive media, against the aluminum surface at high pressure. This action smooths out the surface by removing minor imperfections, tool marks, and machining lines, resulting in a consistent, matte or satin finish that reduces glare. The finish not only improves the part’s aesthetic appeal with its soft, textured feel but also enhances grip and reduces visible wear over time.
Bead blasting is widely used in industries where a subtle, non-reflective surface is desired, including camera housings, medical devices, electronic enclosures, and architectural hardware. This finish is also valued for its ability to prepare surfaces for subsequent coatings or treatments by providing an even texture that promotes better.
Type 4: Polishing
Polishing is a mechanical process that uses a series of fine abrasives to create a smooth, reflective surface. This finish gives parts a high-gloss, mirror-like appearance for maximum visual impact. It involves multiple stages of abrasive polishing to remove surface defects and achieve the desired smoothness.
While visually striking, this type of finish is more suitable for parts that will not be exposed to rough handling or wear. Within the spectrum of types of aluminum finishes, polishing is best suited for display components and decorative applications.
Type 5: Brushing
Brushing creates a distinctive, directional satin texture with fine abrasive belts. The process produces a series of fine, parallel lines that give the part a unique aesthetic. A brushed finish effectively hides fingerprints and minor scratches, making it both beautiful and practical.
This makes it both attractive and practical for everyday use. Brushed finishes are often seen on kitchen appliances, door handles, laptops, and other products where you want a modern, professional appearance that can stand up to regular handling. It’s a great choice when you want something that looks sleek but still feels durable.
Type 6: Mechanical Finishing
Mechanical finishing refers to a group of physical processes that modify the aluminum surface using abrasion, friction, or impact. These methods include grinding, sanding, buffing, brushing, and polishing. The goal is to improve the texture, appearance, or surface smoothness of the part before further treatments like anodizing or painting.
This type of aluminum finish is ideal for removing machining marks, preparing surfaces for coatings, or achieving specific visual effects. Mechanical finishing allows for a wide range of textures, from rough matte to high-gloss mirror finishes. It is commonly used in industries where surface aesthetics or cleanliness is important, such as consumer electronics, medical devices, and architectural elements.
Type 7: Electroplating Plating
Electroplating applies a thin layer of another metal, such as nickel or chrome, onto the aluminum part using an electric current in a chemical bath. This provides a hard, wear-resistant surface and a unique metallic appearance that is both decorative and functional. The electroplating process can increase the part’s hardness and durability, making it suitable for applications where resistance to wear is critical. It is often used for decorative components, automotive emblems, and industrial tooling.
Type 8: PVD Physical Vapor Deposition Coating
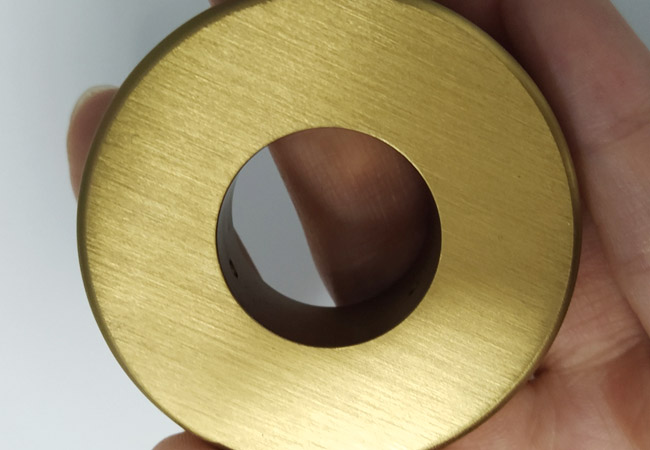
PVD coating, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is an advanced vacuum-based process that applies a very thin but extremely hard and durable film to the surface of aluminum parts. The process begins by placing both the aluminum part and the coating material inside a vacuum chamber. The coating material, usually a metal such as titanium, zirconium, or chromium, is heated until it turns into vapor. This metal vapor then condenses and bonds onto the aluminum surface at the atomic level, creating a strong, even, and highly wear-resistant coating.
PVD is that it provides excellent resistance to scratches, corrosion, and oxidation while adding almost no thickness to the part. This makes it suitable for components that require precise dimensions. PVD coatings also offer rich, metallic finishes in colors such as gold, black, silver, bronze, and even rainbow tones. These qualities make it ideal for high-end consumer electronics, luxury watch cases, decorative hardware, and surgical tools. Unlike traditional plating or painting, PVD is considered environmentally friendly because it does not produce harmful chemical waste.
Choosing the appropriate surface treatment depends on a number of factors, including the part’s application, desired appearance, and functional requirements. Understanding the capabilities of different types of aluminum finishes allows engineers and machinists to select the most effective solution for their specific CNC machining project. The following is a summary of the 8 types of Aluminum Finishes.
| Aluminum Finish | Process Description | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anodizing | An electrochemical process that converts the aluminum surface into a durable, porous oxide layer, allowing for color customization and increased corrosion resistance. | Hard, corrosion-resistant, dye-absorbent, won’t peel or chip. | Consumer electronics, architectural parts, military components. |
| Powder Coating | A dry powder is applied and cured with heat to form a hard, protective layer. Offers a wide selection of colors and textures. | Strong environmental resistance, vibrant colors, high durability. | Automotive parts, industrial machinery, outdoor furniture. |
| Bead Blasting | High-pressure abrasive blasting (usually with glass beads) creates a smooth, uniform matte or satin surface. | Hides imperfections, provides a non-reflective finish, soft tactile feel. | Camera housings, medical devices, components requiring low glare. |
| Polishing | A mechanical process using fine abrasives to create a mirror-like, reflective surface. | Highly aesthetic, glossy finish for maximum visual impact. | Decorative parts, luxury components, display units. |
| Brushing | Abrasive belts create fine, directional lines for a satin-like surface. | Hides fingerprints and minor scratches, provides a modern, sleek look. | Kitchen appliances, consumer electronics, architectural hardware. |
| Mechanical Finishing | Physical surface treatments like grinding, sanding, buffing, or brushing to alter texture and prep for other finishes. | Improves surface appearance and uniformity, prepares for coatings, customizable textures. | Consumer electronics, architectural features, medical devices. |
| Electroplating | Uses electric current to deposit a thin layer of another metal (nickel, chrome) onto the aluminum surface in a chemical bath. | Decorative metallic appearance, increased hardness, good wear resistance. | Automotive trims, decorative fixtures, industrial parts. |
| PVD Coating | Metal vapor in a vacuum chamber deposits a thin, extremely durable layer on the surface. | Superior scratch and corrosion resistance, thin film adds no bulk, multiple color options, eco-friendly. | Luxury watches, electronics, surgical tools, premium hardware. |
In Conclusion
Selecting the right surface finish is essential to ensure both the performance and appearance of your CNC aluminum parts. VMT provides professional support and top-tier finishing solutions to help your components meet the highest standards. As a specialized CNC machining factory, VMT offers a comprehensive range of services including CNC milling, lathe turning, mill-turn machining, Swiss turning, five-axis machining, and rapid prototyping. In addition, we deliver complete surface treatments such as heat treatment, PVD coating, anodizing, polishing, sandblasting, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aluminum Finishes
Type of Anodized Aluminum Finishe
There are three main types of anodized aluminum finishes: Type I uses chromic acid and offers a thin, corrosion-resistant layer; Type II uses sulfuric acid and allows for dyeing in various colors; Type III, or hardcoat anodizing, creates a thicker and more durable layer suitable for high-wear applications. Each type serves different functional and aesthetic purposes.
Types of Black Finishes for Aluminum
Common black finishes for aluminum include black anodizing for durability, black powder coating for a consistent matte look, black wet paint for small batches, black chromate conversion coating for conductivity, and black electroplating for a glossy appearance. Each offers unique benefits depending on the application requirements.
What is the Best Finish for Aluminum?
The best finish for aluminum depends on the application. Anodizing is widely preferred for its durability, corrosion resistance, and color options. Powder coating is excellent for color consistency and scratch resistance. For conductive or aerospace parts, chemical conversion coating is often best. Overall, anodizing is the most versatile.
What is the Most Common Type of Surface Treatment for Aluminum?
Anodizing is the most common surface treatment for aluminum. It enhances corrosion resistance, allows color customization, and improves surface hardness. This finish is widely used in aerospace, electronics, and consumer products due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness in both functional and decorative applications.
How to get Different Finishes on Aluminum?
Different finishes on aluminum can be achieved through methods such as mechanical treatments like brushing or bead blasting, chemical treatments like acid etching or electropolishing, and coating methods like anodizing, powder coating, or wet painting. The right choice depends on function, appearance, and production volume.