Choosing the wrong manufacturing process can waste time, increase costs, and compromise product quality. Every project demands precision, speed, and the right production method.
Both 3d printing vs cnc machining have unique strengths. 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping and intricate designs, while CNC machining offers unmatched precision, repeatability, and superior surface finish for mass production.Do you know which one is truly better for your project?
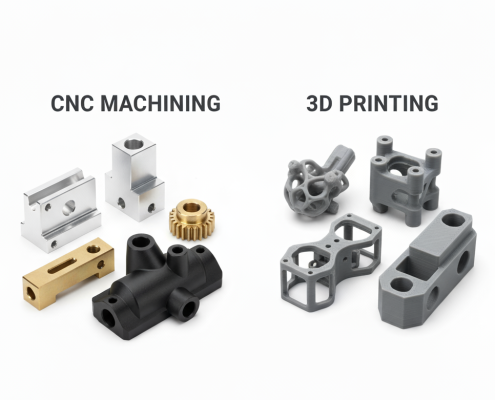
What Is CNC Machining and How Does It Work?
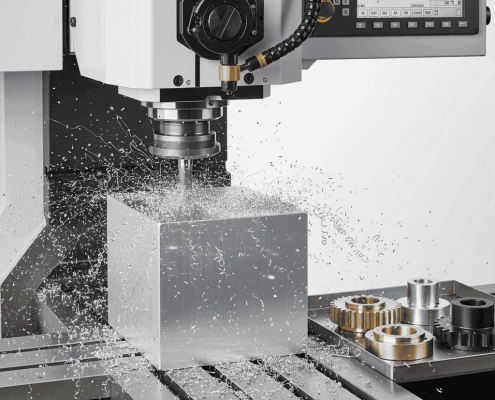

CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses programmed cutting tools to remove material from a solid block. It can process aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, brass, and engineering plastics with high accuracy and repeatability. Common terms in CNC machining include spindle speed, feed rate, cutting depth, and toolpath optimization—all critical for achieving consistent precision in aerospace, automotive, and electronics components.
What Is 3D Printing and How Does It Work?
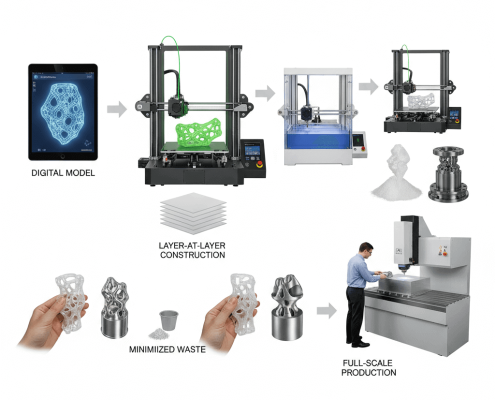

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer using digital models. It works with polymers, resins, and metal powders through methods such as FDM, SLA, SLS, and DMLS. This process minimizes waste and accelerates prototype development. It allows engineers to validate designs quickly before moving to CNC machining for full-scale production.
What’s the Difference Between CNC Machining and 3D Printing?
Both methods deliver functional parts, yet their fundamentals differ: CNC removes material, while 3D printing adds it. This contrast affects accuracy, material options, and cost.
| Aspect | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
| Manufacturing Type | Subtractive | Additive |
| Accuracy | ±0.01 mm | ±0.1 mm typical |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, polished | Layered, requires post-processing |
| Material Variety | Metals, plastics, composites | Limited polymers and metal powders |
| Production Speed | Slower for prototypes | Faster for one-off models |
| Scalability | Ideal for mass production | Best for small batches |
| Waste | High but recyclable | Minimal |
| Cost Efficiency | Better at scale | Cheaper for prototypes |
Which Is Better for Accuracy and Surface Finish?
CNC Machining: CNC machining delivers exceptional accuracy and a superior surface finish. Tolerances often reach ±0.01mm, perfect for medical and optical parts. Surfaces can be smooth as Ra 0.4 μm, ideal for visible parts and precise mechanical fits.
3D Printing: While 3D printing has improved, parts often have visible layer lines, even after polishing. These lines can affect appearance and function, especially where smooth surfaces or high precision are needed.
For critical appearance and exact size, CNC machining is the clear winner. It provides unmatched control over surface quality and very tight tolerances that 3D printing can’t consistently match.
Which Is Better for Design Complexity?
CNC Machining: CNC is limited by cutting tools but makes strong parts with excellent mechanical properties. It ensures tight fits and superior performance. When function and accuracy matter most, CNC is the professional’s choice.
3D Printing: 3D printing truly shines in making complex designs. It can create hollow spaces, lattice structures, and unique organic shapes that CNC can’t. This allows for lightweight parts and custom medical implants.
3D printing offers unmatched freedom for complex and organic designs. But for strong, precise, and functional parts, CNC machining is superior, despite its design limits.
Which Is Better for Cost Efficiency?
CNC Machining: CNC has higher initial setup costs for programming and tools. However, for large production runs, it becomes very cost-effective. As the process is optimized, unit costs drop, making it ideal for high-volume, precision manufacturing.
3D Printing: 3D printing keeps setup and material costs low for single parts or small batches. It doesn’t need special fixtures and can make prototypes in hours, perfect for quick testing or custom items.
3D printing is cheaper for early designs and small custom orders. But for large-scale, high-precision production, CNC machining is more cost-effective overall.
Which Is Better for Prototyping and Production?
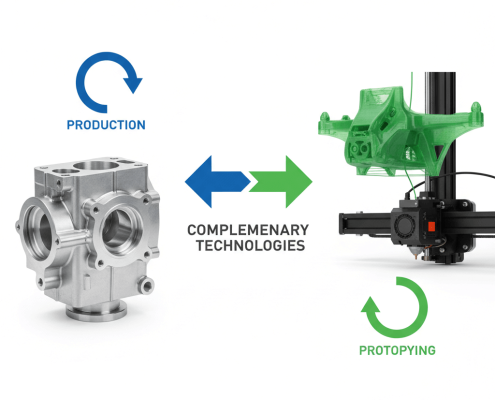
CNC Machining: For actual production, CNC machining is top-tier. Its stability, tight tolerance control, and consistent surface quality mean thousands of parts will be exactly the same. It provides the strength and durability needed for finished products.
3D Printing: 3D printing speeds up early product development. Engineers can get working prototypes fast, quickly finding flaws before using expensive materials. This saves time and money in the initial stages.
3D printing is great for quick prototypes. But for reliable, high-quality mass production, CNC machining is the best. Many companies use both: 3D printing for ideas, and CNC machining for the final product.
Which Is Better for Material Variety?
CNC Machining: CNC machining works with a vast array of materials available in solid block or sheet form. This includes almost all metals and many engineering plastics. If a material exists in bulk, CNC can typically cut it.
3D Printing: 3D printing offers a growing selection of specialized resins and powders. While diverse, its material options are generally limited to specific polymers, metals, and composites designed for additive processes. Some common engineering materials aren’t available for 3D printing.
CNC machining generally offers a broader and more established range of industrial-grade materials. While 3D printing’s material science is rapidly advancing, CNC still leads in sheer material versatility for high-performance applications.
How to Decide Which Is Better for Your Project?
1. Accuracy and Surface Finish
Choose CNC: When you need extremely tight tolerances and the smoothest surface finish.
Choose 3D Printing: When medium accuracy is acceptable, and visible layer lines are not an issue.
2. Design Complexity
Choose CNC: When structural strength and high mechanical performance are the main goals, using conventional geometry.
Choose 3D Printing: When the design requires complex internal features or organic shapes demanding high design freedom.
3. Cost Efficiency
Choose CNC: Best for high-volume production. Low unit cost outweighs the higher initial setup.
Choose 3D Printing: Most cost-effective for single pieces or small custom orders. Ideal for rapid, low-cost iterations.
4. Prototyping and Production
Choose CNC: Essential for final product manufacturing. Requires maximum stability and perfect consistency.
Choose 3D Printing: Best for concept validation and functional prototyping to quickly find design flaws.
5. Material Variety
Choose CNC: When the part must use a specific, industrial-grade bulk material. Offers the broadest range.
Choose 3D Printing: When material choice is limited to specialized resins or powders formulated for additive processes.
| Decision Factor | Best Choice | When to Choose CNC Machining | When to Choose 3D Printing |
| 1. Accuracy and Surface Finish | Depends on precision level | When you need extremely tight tolerances and the smoothest surface finish | When medium accuracy is acceptable and visible layer lines are not an issue |
| 2. Design Complexity | Depends on geometry type | When structural strength and mechanical performance are priorities using conventional geometry | When designs require complex internal features or organic shapes demanding high design freedom |
| 3. Cost Efficiency | Depends on production volume | Best for high-volume production; low unit cost outweighs higher initial setup | Most cost-effective for single pieces or small custom orders; ideal for rapid, low-cost iterations |
| 4. Prototyping and Production | Depends on project stage | Essential for final product manufacturing; ensures maximum stability and perfect consistency | Best for concept validation and functional prototyping to quickly identify design flaws |
| 5. Material Variety | Depends on required materials | Offers the broadest range of industrial-grade metals and plastics | Limited to specialized resins or powders for additive manufacturing |
Start Your Project at VMT
Whether you need high-precision CNC machining or rapid 3D printed prototypes, VMT offers complete support from design to delivery. Our experienced engineers can guide you in choosing the most efficient and cost-effective method between CNC machining and 3D printing.Contact us now to get a free quote!

Summary
There’s no single winner — CNC machining delivers precision, strength, and consistency, while 3D printing offers speed, creativity, and freedom in design. The best solution depends entirely on your project’s needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can these two technologies be used simultaneously?
Yes, they can. Hybrid machines combine both, or 3D printing creates a near-net shape part which is then finished with CNC machining for tighter tolerances.
Is CNC harder than 3D printing?
CNC is generally considered harder. It requires more setup, tooling knowledge, and manual programming of tool paths than the largely automated “slice and print” process of 3D printing.
Will 3D printing replace CNC machining?
No, it is highly unlikely. 3D printing and CNC are complementary. CNC excels at tight tolerances, strength, and mass production, areas where 3D printing still faces limitations.