What Is UNS N02201 According to ASTM B162-99

You encounter UNS N02201 when you work with pure nickel alloys that require low carbon content. This material follows the ASTM B162-99 standard, which sets the rules for rolled nickel plate, sheet, and strip. Many industries choose low-carbon nickel alloys because they offer excellent resistance to corrosion and maintain reliable mechanical strength. Understanding this standard helps you make informed decisions when selecting materials for demanding environments.
Key Takeaways
- UNS N02201 is a low-carbon nickel alloy that meets ASTM B162-99 standards, ensuring high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
- This alloy resists embrittlement and performs well at high temperatures up to 1250°F, making it ideal for chemical processing and harsh environments.
- ASTM B162-99 covers UNS N02201 in various product forms like plate, sheet, strip, and foil, each with specific size and quality requirements.
- Industries such as chemical, aerospace, nuclear, and electronics rely on UNS N02201 for its durability, weldability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Always request a material test certificate to confirm that UNS N02201 products meet ASTM B162-99 standards for safe and reliable use.
UNS N02201 Overview

ASTM B162-99 Scope
You work with UNS N02201 when you need a low-carbon nickel alloy that meets strict industry standards. ASTM B162-99 sets the requirements for rolled nickel plate, sheet, and strip. This standard ensures that the material you select has consistent quality and performance. ASTM B162-99 covers the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing tolerances for these nickel products. You can rely on this standard to guide your selection process for applications that demand high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
ASTM B162-99 helps you verify that the nickel alloy you choose will perform reliably in harsh environments. This standard supports industries such as chemical processing, electronics, and marine engineering.
What is UNS N02201?
UNS N02201, also known as Nickel 201, stands out as a low-carbon version of commercially pure nickel. You may see this alloy listed under several international designations. In Germany, it is called Werkstoff Nr. 2.4068. In Japan, you find it as JIS NW 2201. These designations refer to the same alloy, which offers excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. You can use UNS N02201 in many forms, including seamless and welded tubes, as well as plate, sheet, and strip. The equivalence of these designations means you get consistent quality, no matter where you source the material.
| Designation Type | Designation | Description/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| UNS Number | N02201 | Nickel 201 alloy, low carbon nickel alloy with excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. |
| German Standard (Werkstoff) | 2.4068 | Equivalent to UNS N02201, used in German standards, same alloy grade. |
| Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) | NW 2201 | Equivalent to UNS N02201, same alloy grade under JIS. |
| ASTM/ASME Specifications | ASTM B162, ASME SB162 | Standards covering forms like sheet, strip, plate for UNS N02201 and equivalents. |
| Chemical Composition | Ni 99.0% min, C 0.02% max | Consistent across UNS N02201, Werkstoff 2.4068, and JIS NW 2201. |
| Mechanical Properties | Yield Strength ~14900 psi, Melting Point 1435-1446°C | Comparable mechanical properties across designations. |
| Applications | Marine, offshore engineering | All designations used interchangeably in similar industrial applications due to equivalence. |
Distinction from UNS N02200
You may wonder how UNS N02201 differs from UNS N02200 (Nickel 200). The main difference lies in the carbon content and thermal stability. UNS N02201 contains a maximum of 0.02% carbon, while UNS N02200 allows up to 0.15%. This lower carbon content in UNS N02201 gives you better resistance to graphitization at high temperatures. As a result, you can use UNS N02201 in environments up to 1250°F (677°C), while UNS N02200 is suitable only up to 600°F (315°C). Both alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance and similar mechanical properties, but you should choose UNS N02201 when you need high temperature performance and minimal carbon contamination.
| Aspect | UNS N02200 (Nickel 200) | UNS N02201 (Nickel 201) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | Maximum 0.15% | Maximum 0.02% |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Up to 600ºF (315ºC) | Up to 1250ºF (677ºC) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Outstanding in caustic soda, alkalis, reducing environments; limited in stagnant seawater | Similar corrosion resistance; better for high temperature and carbon-sensitive environments |
| Mechanical Properties | Highly ductile, ferromagnetic, weldable | Similar mechanical properties |
| Industrial Applications | Aerospace, chemical and petrochemical processing, food processing, marine, water treatment | Same sectors, preferred for high temperature and low carbon contamination needs |
When you select UNS N02201, you ensure reliable performance in high-temperature and carbon-sensitive environments. This makes it a preferred choice for chemical processing, synthetic fiber production, and electronics manufacturing.
Properties
UNS N02201 Chemical Composition
You need to know the exact chemical makeup when you select a nickel alloy for demanding environments. ASTM B162-99 sets strict limits for the elements in UNS N02201. This alloy contains mostly nickel, with very low carbon to prevent unwanted reactions at high temperatures. The table below shows the typical chemical composition:
| Element | Content (Weight %) |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 99.0 min |
| Carbon (C) | 0.02 max |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.25 max |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.40 max |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.35 max |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.35 max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.01 max |
You can see that nickel dominates the composition. The low carbon content helps you avoid graphitization and embrittlement, especially at high temperatures. This makes UNS N02201 a reliable choice for applications where purity and stability matter.
Mechanical Properties
When you choose UNS N02201, you get a material with a balance of strength, ductility, and toughness. The mechanical properties depend on the processing condition, such as annealed or cold worked. In the annealed state, you find that this alloy offers moderate strength and high ductility. The table below compares the mechanical properties of UNS N02201 with UNS N02200 and other high-purity nickel alloys:
| Property | UNS N02201 (Nickel 201, Annealed) | UNS N02200 (Nickel 200, Annealed) | High Purity Nickel Alloys (Annealed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (ksi) | 57.7 | 62 | 53.5 – 98.5 |
| Yield Strength (ksi) | 17.3 | 18 | 15.5 – 96.5 |
| Elongation (%) | 42 | 44 | 30 – 45 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 110 | 110 | 110 – 209 (varies by temper) |
You can see that UNS N02201 and UNS N02200 have similar mechanical properties. Both alloys provide good ductility and moderate strength. When you need higher strength, you can use cold worked material, which increases both tensile and yield strength. The chart below shows how tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation compare among these nickel alloys:
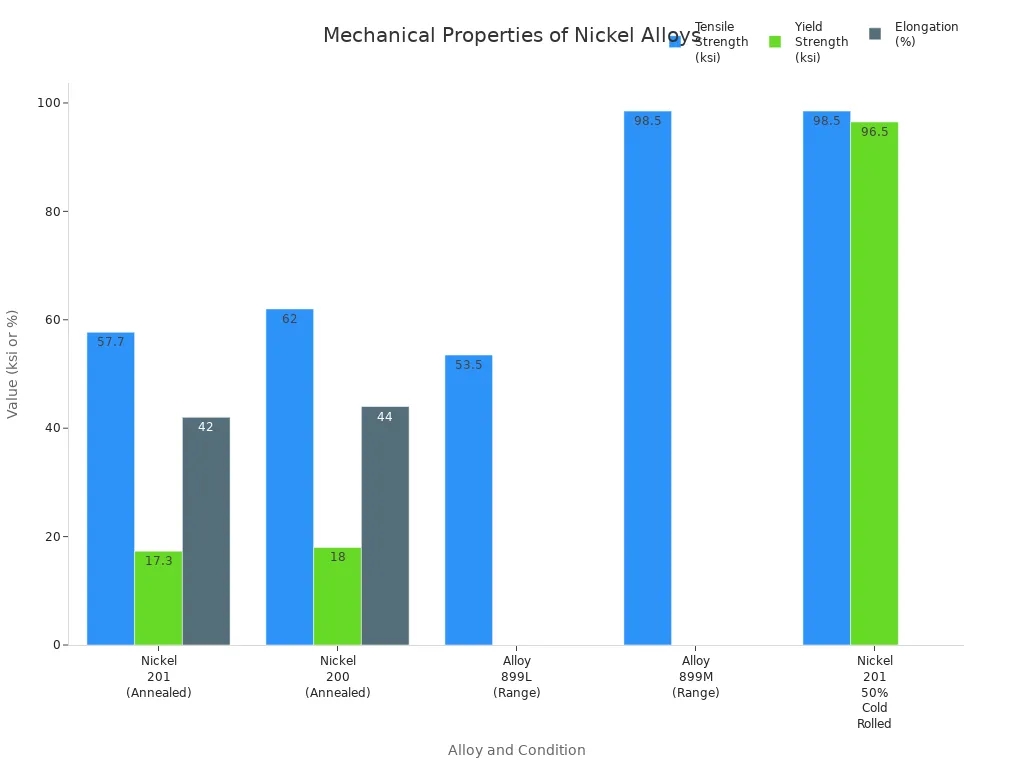
You can rely on UNS N02201 for applications that require both formability and resistance to cracking. The alloy’s mechanical properties make it suitable for forming, welding, and machining.
Corrosion Resistance
You often choose UNS N02201 for its outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in caustic and alkaline environments. This alloy resists attack from most acids and alkalis, making it a top choice for chemical processing. The table below highlights key corrosion resistance data:
| Property / Condition | UNS N02201 (Nickel 201) Corrosion Resistance Details |
|---|---|
| Corrosion rate in caustic soda (up to 73%) | Less than 0.025 mm/year (1 mpy) |
| Corrosion rate above 73% caustic | Slight increase in corrosion rate |
| Caustic stress corrosion cracking (SCC) | Resistant at all concentrations and temperatures up to ~290°C (550°F) |
| Recommended temperature for use | Above 300°C (572°F) to avoid graphite formation and embrittlement |
| Carbon content | Low (max 0.02%) to prevent intergranular corrosion at high temperatures |
| Resistance in alkaline solutions | Excellent, but susceptible if chlorate concentration is high due to chloride formation |
| Certification | Approved for pressure vessel use up to 600°C (1112°F) |
| Corrosion resistance in oxidizing/reducing media | Good once passivation oxide layer forms |
You can use UNS N02201 in caustic soda production, food processing, and electronics manufacturing. The alloy resists stress corrosion cracking and maintains its integrity even at elevated temperatures. You should avoid environments with high chlorate concentrations, as these can increase the risk of corrosion.
When you need a material that stands up to harsh chemicals and high temperatures, UNS N02201 gives you peace of mind. Its low carbon content and stable oxide layer protect your equipment and extend service life.
Applications

Industrial Uses
You often see UNS N02201 used in environments that demand high corrosion resistance and stability at elevated temperatures. This alloy works well in chemical processing plants, especially where you handle caustic alkalis and acids. You find it in equipment for sodium hydroxide production, viscose rayon manufacturing, and soap making. The low carbon content prevents embrittlement, so you can use it in reactors that process fluorine and hydrocarbons. Its good formability and weldability allow you to shape it into seamless tubes, pipes, and complex components for demanding industrial systems.
| Application Field | Typical Conditions | Failure Mode | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nuclear heat exchange | 300°C/15 MPa boric acid | Grain boundary erosion | Enhanced solution treatment |
| Petrochemical cracking | 550°C H₂S environment | Sulfide stress corrosion | Surface nanocrystallization |
| Aerospace LOX systems | Liquid oxygen transfer | Low-temperature brittleness | Cold-working deformation ≤30% |
You select UNS N02201 for these uses because it resists corrosion in reducing media, maintains strength up to 600°C, and avoids embrittlement due to its low carbon content.
Industries Served
You find this alloy in a wide range of industries. Chemical processing companies use it for storage tanks, piping, and heat exchangers. The petrochemical industry relies on it for cracking units and reactors. Nuclear power plants use it in heat exchange systems. Aerospace manufacturers choose it for liquid oxygen transfer lines. You also see it in electronics, food processing, and new energy equipment. Each industry values the alloy’s ability to withstand harsh chemicals and high temperatures.
- Chemical processing
- Petrochemical
- Nuclear energy
- Aerospace
- Electronics manufacturing
- Food processing
- New energy equipment
Comparison with Other Nickel Alloys
When you compare UNS N02201 to other nickel alloys, you notice several advantages. Unlike UNS N02200, which has higher carbon content, UNS N02201 resists embrittlement at higher temperatures. This makes it a better choice for applications above 600°F (315°C). Other nickel alloys may offer higher strength or specialized resistance, but they often lack the combination of purity, weldability, and high-temperature stability you get with UNS N02201. You should choose this alloy when you need reliable performance in caustic, acidic, or high-temperature environments.
Manufacturing and Supply
Product Forms
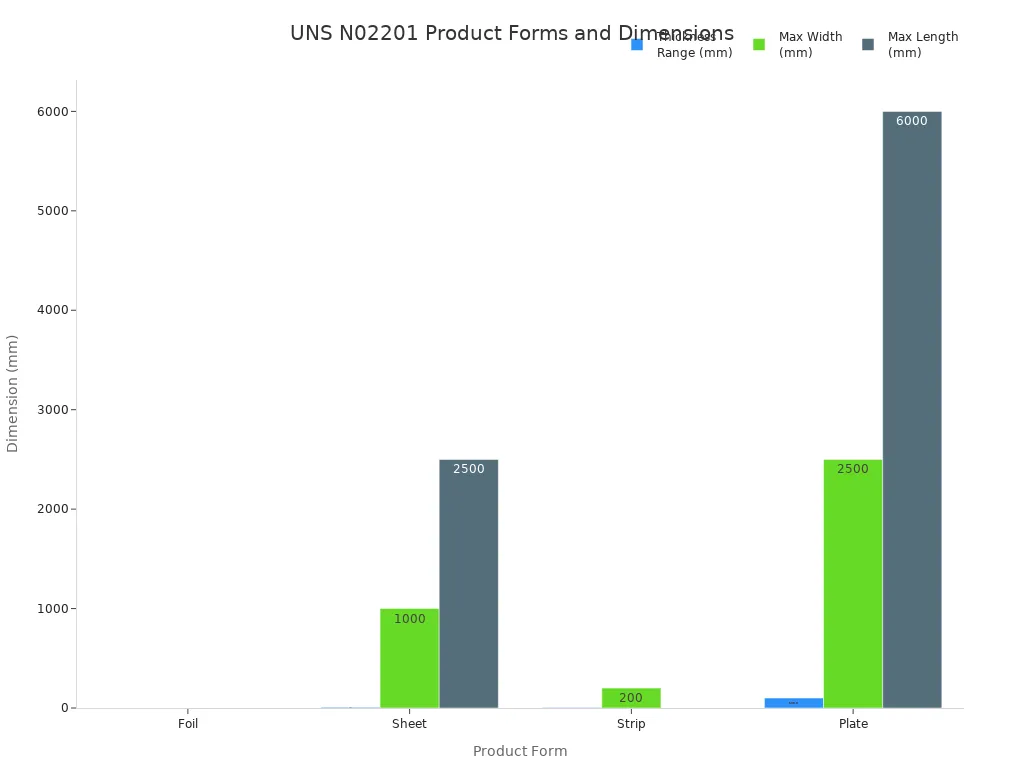
You can choose from several product forms when you need nickel alloys for industrial use. ASTM B162-99 defines the main forms as plate, sheet, strip, and foil. Each form has specific thickness, width, and length ranges. The table below shows typical dimensions for each product form:
| Product Form | Thickness Range | Width Range | Lengths | Typical Dimensions (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foil | < 0.15 mm | N/A | N/A | Classified as foil | Thickness less than 0.15 mm |
| Sheet | 0.15–6.35 mm | ≥ 600 mm (24″) | 2000–2500 mm | 0.5–2.0 mm thick, ~1000 mm wide | Cold-rolled, annealed |
| Strip | < 5.00 mm | < 600 mm (24″) | Coils | 0.10–0.30 mm thick, 100–200 mm wide | Supplied in coils, cold-rolled, annealed |
| Plate | ≥ 5.00 mm | 10–2500 mm | 2000–6000 mm | 5–100 mm thick, 10–2500 mm wide | Hot-rolled, soft annealed, various finishes |
Plate sizes often include 1000×2000 mm, 1220×2440 mm, and 1500×3000 mm. Sheet and strip are usually cold rolled and annealed, while plates are hot rolled and can have different finishes.
Compliance with ASTM B162-99
You must ensure that your material meets ASTM B162-99 requirements before using it in critical applications. This standard covers chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances. Manufacturers test each batch for purity and strength. They also check thickness, width, and surface finish. You should always request a material test certificate. This document proves that your product meets the standard. Quality assurance teams inspect each plate, sheet, or strip to confirm compliance. Reliable suppliers provide full traceability from raw material to finished product.
Start Your CNC Machining Project at VMT
You can start your CNC machining project with confidence at VMT. When you work with nickel alloys, you need the right tools and parameters. Type C-2 carbide for roughing and drilling, and Type C-3 for finishing. You benefit from the alloy’s good ductility and strength, but you may need more power for cold forming. VMT’s team helps you select the right process and tools for your project.
Tip: Always discuss your specific requirements with VMT’s engineers. They can recommend the best machining strategy for your application.
Frequently Asked Questions About UNS N02201
What is the main advantage of UNS N02201 over other nickel alloys?
You get better resistance to graphitization at high temperatures with UNS N02201. Its low carbon content helps you avoid embrittlement, making it ideal for applications above 600°F (315°C).
What forms does ASTM B162-99 cover for UNS N02201?
You can find UNS N02201 as plate, sheet, strip, and foil under ASTM B162-99. Each form meets strict requirements for thickness, width, and surface finish.
What industries use UNS N02201 most often?
You see UNS N02201 in chemical processing, electronics, aerospace, and food processing. These industries value its corrosion resistance and stability at high temperatures.
What do cumentation should you request to ensure compliance?
Always ask for a material test certificate. This document proves your UNS N02201 meets ASTM B162-99 standards for composition, mechanical properties, and dimensions.
What is the UNS Code for INCONEL?
INCONEL is a trademark for a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys, and each grade has its own Unified Numbering System (UNS) designation. Some common examples are:
-
INCONEL 600 – UNS N06600
-
INCONEL 601 – UNS N06601
-
INCONEL 625 – UNS N06625
-
INCONEL 718 – UNS N07718
-
INCONEL X-750 – UNS N07750



