Micro-arc Oxidation: An Ultimate Guide
Is your metal part struggling with rust, wear, or poor performance? Are standard coatings just not cutting it? Micro-arc oxidation offers a superior solution!
Micro-arc oxidation is an electrochemical surface treatment that creates a hard, dense, and corrosion-resistant ceramic layer on light metals and their alloys like Micro-arc oxidation Aluminum, Micro-arc oxidation Magnesium, and Micro-arc oxidation Titanium. It significantly enhances wear resistance, corrosion resistance, insulation, and biocompatibility, providing high-performance protection for demanding applications.
Want to know how MAO can boost your product’s durability and performance? Let’s keep reading!
What is Micro-Arc Oxidation?
Micro-arc oxidation is a cutting-edge electrochemical process that forms a robust ceramic coating on specific metal surfaces through controlled high-voltage plasma discharges within an electrolyte. Unlike conventional anodizing, MAO involves higher voltages that cause micro-sparks, leading to the growth of a thicker, denser, and more crystalline oxide layer.
This unique formation mechanism results in superior properties compared to traditional surface treatments like hard anodizing or electroplating. For instance, while standard anodizing produces a porous layer, MAO creates a highly integrated and less permeable coating. The metallurgical bond formed between the ceramic layer and the base metal ensures exceptional adhesion, crucial for parts subjected to high stress and wear in precision CNC machining applications.

Which Materials Can Undergo Micro-Arc Oxidation Treatment?
Micro-arc oxidation is a surface treatment process designed for valve metals and their alloys. It creates a ceramic layer that improves surface hardness, wear resistance, and protection against corrosion. Each material benefits differently from MAO depending on its natural properties and applications.
1. Micro-Arc Oxidation Aluminum
MAO creates a tough and wear-resistant surface on aluminum. This is especially useful for parts that need to remain lightweight while handling friction and harsh conditions. It is commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries, where aluminum components must maintain strength without adding weight. MAO performs better than traditional anodizing and is ideal for CNC machined aluminum parts.
3. Micro-Arc Oxidation Titanium
Titanium is well known for its corrosion resistance and compatibility with the human body. MAO further strengthens its surface by increasing wear resistance and improving its ability to bond with bone tissue. This is valuable in medical implants and aerospace parts where reliability and longevity are critical.
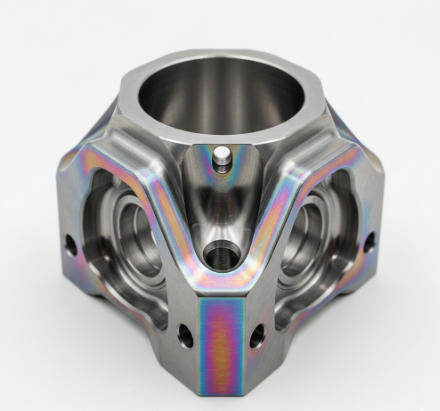

3. Micro-Arc Oxidation Zirconium
Zirconium is often used in medical and nuclear applications. MAO treatment boosts its resistance to heat and chemical damage. The ceramic layer allows zirconium parts to last longer in high-temperature or corrosive environments, such as reactors and surgical tools.
4. Micro-Arc Oxidation Tantalum
Tantalum is naturally bio-safe and corrosion-resistant. MAO improves its surface further, making it ideal for medical devices and equipment used in chemical processing. The added layer increases strength and reduces surface wear during use.
5. Micro-Arc Oxidation Niobium
Niobium is used in electronics and aerospace systems. MAO treatment gives its surface better electrical insulation and resistance to wear. This allows it to perform better in environments where precision and surface stability matter.
6. Micro-Arc Oxidation Magnesium
Magnesium is one of the lightest structural metals but is naturally prone to corrosion. MAO forms a dense ceramic layer that protects it from moisture and chemical exposure. This makes it more suitable for products like portable electronics, automotive parts, and other applications that benefit from low weight and high durability

The following is the material of undergo micro-arc oxidation treatment comparison table.
| Material | Benefits of MAO Treatment | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Hard and wear-resistant surface | Aerospace, automotive, CNC machined parts |
| Magnesium | Strong corrosion protection and surface durability | Portable electronics, vehicle components |
| Titanium | Enhanced wear resistance and biocompatibility | Medical implants, aerospace parts |
| Zirconium | Improved heat and chemical resistance | Nuclear systems, surgical tools |
| Tantalum | Strong surface and bio-safety | Medical devices, chemical processing tools |
| Niobium | Better insulation and surface stability | Electronics, aerospace, precision systems |
How Is the Micro-Arc Oxidation Process Applied to Aluminum?
The Micro-Arc Oxidation process for aluminum involves several important steps that help create a strong, high-performance ceramic coating on the surface of aluminum parts.
1. Pre-Treatment
Before the MAO process begins, aluminum parts must be properly cleaned and prepared. This step is very important to make sure the coating sticks well and forms evenly. The surface is cleaned to remove oil, grease, or dirt. Then, it may go through additional treatments like degreasing or etching to get rid of any remaining residues. For CNC machining aluminum parts, extra care is taken to remove leftover cutting fluids or tiny burrs to avoid coating defects.
2. MAO Treatment
Once the surface is clean, the aluminum part is placed into a special alkaline solution that acts as the electrolyte. The aluminum part is connected as the anode, and a counter electrode is added. High voltage electricity is applied to create tiny sparks on the aluminum surface. These sparks generate plasma, which transforms the surface of the aluminum into a ceramic oxide layer. The process is carefully controlled by adjusting the power supply, treatment time, and the type of electrolyte. These factors affect the final coating’s thickness, roughness, and strength.
3. Post-Treatment
After the MAO treatment, the aluminum part is washed to remove any leftover chemicals. Depending on how the part will be used, extra steps might be added. This can include drying, sealing to improve corrosion resistance, or adding color for appearance. To make sure the coating meets performance standards, tests are done. These may include measuring the coating’s thickness and hardness, checking surface smoothness, and testing for corrosion resistance using salt spray.
What Unique Properties Do Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings Have?
Micro-arc oxidation creates a strong ceramic layer on metal surfaces. This coating improves how parts perform in harsh or demanding conditions. Here are the key benefits of MAO coatings explained in simple terms.
Hard and Resistant to Wear: MAO coatings make the surface of the metal very hard, almost like ceramic. This helps reduce scratches and wear, making parts last longer. For example, aluminum treated with MAO becomes much more durable. This is great for CNC parts used in machines or tools that face heavy use.
Excellent Protection from Rust and Corrosion: The MAO layer blocks water, salt, and chemicals from reaching the metal. This keeps the part from rusting or corroding over time. It is especially useful for magnesium, which normally corrodes easily without this type of protection.
Good Electrical Insulation: Because MAO forms a ceramic layer, it does not conduct electricity. This makes it useful for electronic parts that must be insulated to prevent short circuits or electric failures.
Can Handle Heat and Sudden Temperature Changes: MAO coatings stay stable at high temperatures. They also resist cracking when the part heats up or cools down quickly. This is helpful for parts used in engines, heating systems, or other high-temperature environments.
Strong Surface Bonding and Smooth Finish: MAO coatings bond tightly to the metal and do not peel off easily. The surface can be made rough or smooth depending on the need. This is important for parts that require strong surfaces and good precision.
In Which Industries Is Micro-Arc Oxidation Widely Used?
Micro-arc oxidation is valued across many industries for its ability to improve surface strength, corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and biocompatibility. Below is a summary of key industries and how they apply Micro-arc oxidation technology:
| Industry | Typical Applications | Benefits of MAO Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine parts, brake systems, lightweight frames (Aluminum, Magnesium) | Improved wear and corrosion resistance, enhanced fatigue strength, better fuel efficiency |
| Aerospace | Structural components, engine parts, satellite housings (Aluminum, Titanium) | High temperature resistance, lightweight protection, durability in extreme conditions |
| Medical Devices | Implants, dental tools, surgical instruments (Titanium) | Excellent biocompatibility, enhanced osseointegration, long-term corrosion protection |
| Electronics | Enclosures, heat sinks, connectors (Aluminum) | Electrical insulation, heat resistance, protection for sensitive components |
| Industrial Equipment | Valves, pumps, molds, textile machine parts | High wear and corrosion resistance, reduced maintenance, extended service life |
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphone housings, internal frames (Aluminum, e.g., iPhones) | Scratch resistance, premium feel, enhanced appearance and surface durability |
| Optical Technology | Precision instrument parts | Smooth, durable coatings that ensure long-term accuracy and performance |
Start Your Part Post-Processing – Micro-arc Oxidation Project
At VMT, we have over 15 years of CNC machining expertise to provide exceptional precision and finish to your components. We have over 100 advanced machines, including 4-axis and 5-axis imported CNC machining centers and turn-mill machines, ensuring fast delivery of many products within 24 hours. Our team of 6 engineers with over 20 years of experience provides free design services to ensure parts achieve exceptional precision and aesthetics.
In addition, 2 professional engineers are responsible for fine management of surface treatments, including advanced aluminum micro-arc oxidation, magnesium micro-arc oxidation and titanium micro-arc oxidation processes. We have obtained ISO 9001:2005, IATF 16949 and SGS certifications to ensure that all your custom metal and plastic CNC machining needs meet the highest standards of quality and reliability. Contact us today for a free quote!
Frequently Asked Questions About Micro-arc Oxidation
How Does EDTA Affect the Micro-arc Oxide Layer?
EDTA, a chelating agent, can influence the composition and stability of the electrolyte during MAO. It may enhance coating uniformity and reduce pore size by controlling metal ion activity in the solution. However, excessive EDTA can weaken the oxide layer by interfering with plasma discharge or altering the coating’s structure.
What Colors and Finishes are Possible with Micro-arc Oxidation?
MAO coatings typically range from light gray to dark gray or black, depending on the metal, electrolyte, and process parameters. Some electrolytes can produce brown, blue, or gold hues. The finish is usually matte or slightly rough due to the ceramic nature but can be polished or sealed for smoother or shinier surfaces.
How Does Micro-arc Oxidation Compare to Anodizing Regarding Corrosion Protection?
MAO offers better corrosion protection than traditional anodizing. The MAO coating is thicker, denser, and ceramic-like, making it more resistant to chemical attack, abrasion, and saltwater exposure. Anodizing provides moderate protection and is more suited for decorative or less demanding applications.
Is Micro-arc Oxidation the same as Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation?
Yes, micro-arc oxidation (MAO) is another name for plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO). Both refer to the same high-voltage electrochemical process that forms ceramic oxide coatings on metals like aluminum, magnesium, and titanium using plasma micro-discharges in an alkaline electrolyte.



