What Is CNC Logo Cutting and How Does It Work?
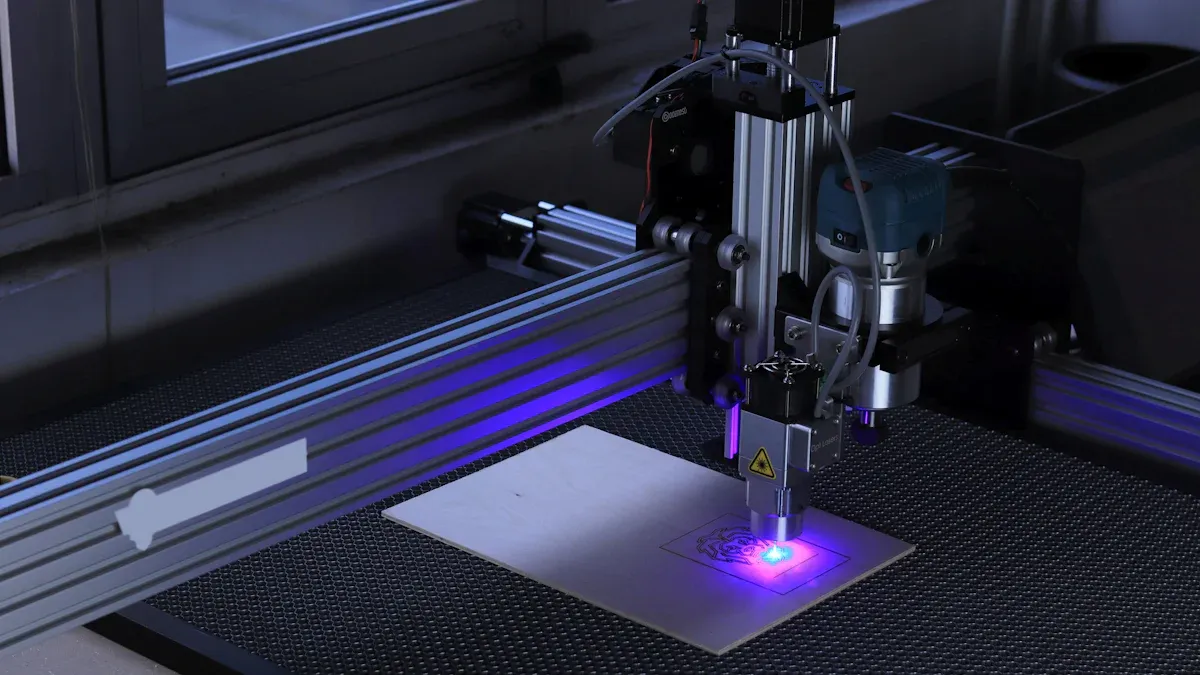

CNC logo cutting uses computer-controlled machines to create precise logo designs from digital files. You start with a digital design, prepare the file, and let advanced machines cut or engrave the material. This process ensures sharp details and consistent results. Different industries, such as automotive, signage, and architecture, rely on CNC logo cutting for accuracy and flexibility.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
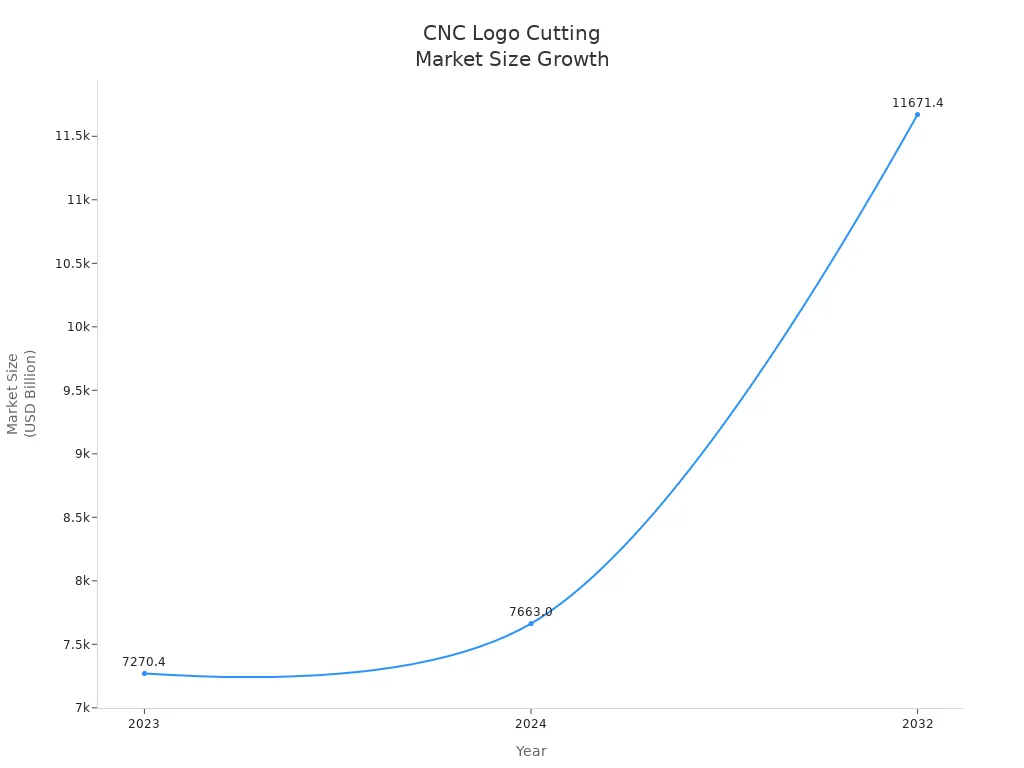
| Market Size (2023) | USD 7,270.4 Billion |
| Market Size (2024) | USD 7,663.0 Billion |
| Projected Market Size (2032) | USD 11,671.4 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2032) | 5.4% |
| Largest Market Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Market Drivers | Automotive Industry Demand, Automation in Emerging Economies |
Precision, advanced technology, and the right materials set CNC logo cutting apart, making it a top choice for detailed branding and manufacturing needs.
Key Takeaways
- CNC logo cutting uses computer-controlled machines to create precise and detailed logos from digital designs, ensuring consistent and sharp results.
- This technology works with many materials like metals, plastics, and wood, offering flexibility for various industries such as signage, automotive, and woodworking.
- You start by preparing a vector-based digital file, which the CNC machine uses to follow exact cutting paths for high accuracy.
- Different CNC machines suit different materials and designs, including laser cutters, routers, milling machines, and waterjets, each with unique strengths.
- CNC logo cutting offers faster production, higher precision, and better repeatability than manual methods, making it ideal for large or complex logo projects.
CNC Logo Cutting Basics

Definition
You use CNC logo cutting to create logos and designs on materials like wood, metal, plastic, and stone. This process relies on a computer numerical control (CNC) machine that follows programmed commands to cut or engrave your design. Unlike laser engraving, which uses light, CNC logo cutting machines move tools or the material itself to shape the logo. You start with a digital design, usually made in CAD software, and the machine translates this into precise movements. This method stands out because it delivers high accuracy, lets you update designs easily, and produces intricate, durable logos. You do not need expensive embossing dies, and you can achieve consistent results with less manual labor.
Tip: CNC logo cutting gives you more control over the final look of your logo, making it ideal for detailed and repeatable branding.
Applications
You find CNC logo cutting in many industries because it offers precision and flexibility. In manufacturing and industrial design, you can use it to engrave metal parts or create detailed steelwork. The advertising and signage industries rely on CNC logo cutting for making 3D letters, acrylic signs, and channel letters. Woodworking shops use it for furniture, doors, and decorative panels. Even the die industry benefits from CNC logo cutting when making molds and metal sculptures.
| Application Area | Primary Uses |
|---|---|
| Sign Making & Advertising | Logo making, 3D letters, acrylic cutting, LED/neon channel letters, molds |
| Woodworking | Doors, furniture, panels, musical instruments, decorative wave plates |
| Die Industry | Copper sculptures, aluminum engraving, metal molds, plastic sheeting |
| Decoration | Acrylic, density board, artificial stone, soft metals like aluminum, copper |
You can see that CNC logo cutting supports a wide range of creative and industrial needs.
Materials
You can choose from several materials for CNC logo cutting, depending on your project. Metals like aluminum, brass, copper, steel, and titanium offer strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Plastics such as ABS, nylon, PEEK, and PTFE (Teflon) are cost-effective and easy to machine. Wood remains a popular choice for its traditional look and natural appeal. CNC machines handle these materials well, letting you create logos that are both precise and visually striking.
| Material Type | Examples | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Steel, Titanium | Strength, durability, precision, corrosion resistance |
| Plastics | ABS, Nylon, PEEK, PTFE (Teflon) | Cost-effective, easy to machine, chemical resistance |
| Wood | Various types | Aesthetic appeal, traditional use |
You benefit from using these materials because CNC logo cutting combines efficiency, accuracy, and the ability to produce complex designs with ease.
Process
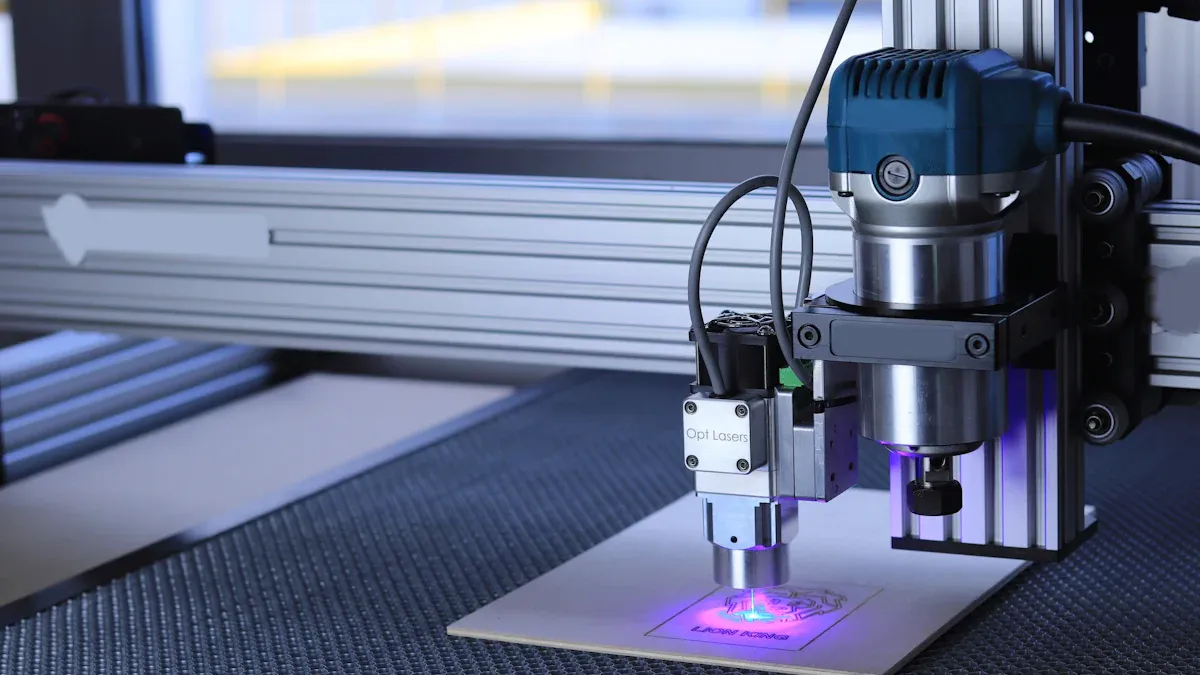

Design Files
You begin CNC logo cutting by preparing a digital design file. This file acts as the blueprint for your logo. Most CNC machines require you to use vector-based formats because these files describe shapes with mathematical precision. Vector files, such as DXF, STEP, and IGES, allow the machine to follow exact paths and curves. If you start with a raster image, like a JPEG or PNG, you need to convert it to a vector format. Raster images use pixels, which can become blurry or jagged when scaled. Vectorization transforms these pixel-based images into crisp, scalable graphics. This step is crucial because CNC machines rely on clean lines and curves to cut accurately.
Tip: Always use high-quality, isolated logos for vectorization. Clean images without background noise produce better results.
You often use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create or edit your logo. After designing, you export the file in a format compatible with your CNC machine. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software then converts this file into G-code, which contains the instructions for the machine’s movements.
| File Type | Description & Use Case | Importance for Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| STEP (.stp) | Neutral format preserving geometric and manufacturing data; widely used for 3D models. | Maintains precise geometry and tolerances, ensuring accurate machining. |
| IGES | Neutral format, older standard; preserves geometry but less preferred than STEP. | Supports precision by conveying geometric data, though less robust than STEP. |
| DXF | 2D line work and technical drawings; used in laser cutting and sheet metal fabrication. | Provides exact planar profiles and annotations critical for accurate 2D cutting paths. |
| DWG | Proprietary AutoCAD format with vectors and metadata; used for detailed technical drawings. | High fidelity for dimensions and multi-sheet documentation, important for detailed designs. |
| STL | Mesh of triangles representing surface geometry; common in prototyping and additive manufacturing. | Lacks parametric and tolerance data, less ideal for high-accuracy CNC but useful for visual/physical mock-ups. |
| Vector (SVG, AI, EPS) | 2D artwork formats; mathematically described curves for logos and text. | Suitable for planar cutting but no 3D data, limiting use to 2D operations. |
| Proprietary CAD (e.g., SLDPRT, IPT) | Native files capturing full design features and parameters. | Require conversion to neutral formats (STEP/IGES) to preserve design intent and ensure CNC compatibility. |
You should choose the right file type for your project. STEP files work best for 3D logos, while DXF files suit 2D cutting. Always check your machine’s requirements before starting.
Machine Types
You have several machine options for CNC logo cutting. Each type uses a different cutting method and works best with certain materials and designs.
| CNC Machine Type | Cutting Method/Mechanism | Suitable Materials | Precision & Complexity | Limitations/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting CNC Machine | Focused laser beam | Wood, plastics, sheet metal | High precision, good for detailed cuts | Limited to max thickness ~2.75 inches; no heat-affected zones but thickness limited |
| CNC Router Machine | Rotating cutting tool on flat surfaces | Wood, plastics, soft metals | Versatile for patterns and flat surface cuts | Noisy operation; mainly 2D/flat surface cutting |
| CNC Milling Machine | Rotary cutters removing material | Metals, wood | High precision, can create complex 3D shapes | More setup required; generally more expensive |
| CNC Plasma Cutting Machine | High-speed plasma arc | Electrically conductive metals | Precise cuts on metals | Produces heat-affected zones; limited to conductive materials |
| CNC Waterjet Cutting Machine | High-pressure water jet | Almost any material | Very versatile, no heat-affected zones | Slower cutting speed, especially on curves |
| Multi-Axis CNC Machine | Multiple axes movement (4+ axes) | Various materials | Greater flexibility and accuracy for complex shapes | Requires professional operation; more complex and expensive |
- Laser cutting machines use a focused beam to cut or engrave. You get sharp details and smooth edges, especially on thin materials.
- CNC routers work well for wood, plastics, and soft metals. You can create patterns, letters, and flat designs.
- CNC milling machines handle metals and wood, letting you produce complex 3D logos with high accuracy.
- Plasma cutters excel at cutting conductive metals quickly, but they create heat-affected zones.
- Waterjet machines use high-pressure water, sometimes with abrasives, to cut almost any material. You avoid heat damage, but the process can be slower.
- Multi-axis machines give you more flexibility. You can cut intricate shapes and angles that standard machines cannot achieve.
Note: Choose your machine based on the material, design complexity, and required precision for your logo.
Technologies
You benefit from recent technological advancements in CNC logo cutting. These innovations improve accuracy, efficiency, and customization.
- Multi-axis machining (5-axis and 6-axis) lets you create complex geometries and detailed logos with fewer setups.
- AI and machine learning optimize tool paths and predict maintenance needs, reducing errors and downtime.
- Digital twin technology allows you to simulate the cutting process virtually. You can spot issues before production starts.
- IoT-enabled machines provide real-time monitoring. You track performance and quality, making adjustments as needed.
- Hybrid machines combine additive manufacturing (like 3D printing) with CNC cutting. You streamline production and enable unique designs.
- Automation and robotics reduce human error and increase productivity.
- Advanced cutting tools, such as diamond-tipped or coated tools, last longer and cut more precisely.
- Sustainability features, like energy-efficient designs and coolant recycling, help you reduce environmental impact.
- Virtual and augmented reality support training and design validation. You can visualize the process and catch errors early.
Smart manufacturing technologies make CNC logo cutting more reliable and sustainable. You achieve higher quality with less waste.
You follow a clear process for CNC logo cutting:
- Prepare or convert your logo into a vector file.
- Import the file into CAD/CAM software and generate G-code.
- Select the right CNC machine and set up your material.
- Run a simulation if available to check for errors.
- Start the machine and monitor the cutting process.
- Inspect the finished logo for quality and accuracy.
By following these steps and using the latest technologies, you ensure your logo meets your design and quality standards.
Comparison
CNC vs. Traditional
When you compare CNC logo cutting to traditional manual methods, you see clear differences in how each approach handles accuracy, complexity, and consistency. CNC machines follow digital templates and programmed instructions, which means every cut matches your design exactly. Manual logo cutting depends on the skill of the operator, so results can vary from one piece to another. If you need to produce many identical logos, CNC logo cutting gives you the repeatability that manual methods cannot match.
| Aspect | CNC Logo Cutting | Manual Logo Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy & Precision | Extremely high precision; follows digital templates | Lower accuracy; depends on operator skill |
| Consistency & Repeatability | Identical results every time | Variability between pieces |
| Complexity & Detail | Handles intricate, complex designs | Limited by hand skill and tools |
| Suitability | Best for high-volume, detailed work | Suited for low-volume, custom work |
| Human Error | Minimal due to automation | Higher risk due to manual control |
Note: CNC logo cutting excels when you need high precision and complex designs, while manual methods work best for simple, custom projects.
Precision
You achieve much higher precision with CNC logo cutting than with manual techniques. CNC machines use G-code instructions to control every movement, so you get tight tolerances and perfect symmetry. Manual cutting often leads to small errors, especially with detailed logos. If your project requires intricate shapes or fine details, CNC logo cutting ensures each piece meets your exact specifications.
- CNC machines follow digital templates, so every cut is accurate.
- Manual methods rely on steady hands, which can introduce mistakes.
- CNC technology allows you to create complex logos with perfect symmetry.
Speed
CNC logo cutting also outpaces manual methods in terms of speed. Once you program the machine, it can run continuously with little supervision. You can finish projects in a few hours that might take days by hand. This fast turnaround is especially helpful for large orders or tight deadlines.
- CNC machines operate at high speeds and can work around the clock.
- Manual cutting requires constant attention and takes longer, especially for complex designs.
- Automated processes reduce setup and adjustment times, so you get your finished logos faster.
If you want to replicate complex designs quickly and accurately, CNC logo cutting is the clear choice. You save time, reduce errors, and ensure every logo looks exactly as you planned.
Advantages of CNC Logo Cutting
Accuracy
You achieve outstanding accuracy with CNC Logo Cutting. The process uses computer-controlled machines that follow digital instructions, so every logo matches your design exactly. Precision in CNC machining means you get consistent results across many parts, not just one. You measure this precision using calibrated gauge parts and statistical quality control methods like Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility (GR&R) and Measurement System Analysis (MSA). These tools help you spot any variation and keep your logos within tight tolerances. Standard tolerances for CNC machining are usually around ±0.13 mm (±0.005 inches), which means your logos will have sharp details and perfect symmetry. Advanced systems like Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) help control the form, orientation, and position of each cut, ensuring your logos always meet the highest standards.
Tip: Consistent accuracy means you can trust every logo to look just like the original design, even in large production runs.
Customization
You can customize almost every aspect of your logo with CNC Logo Cutting. This technology supports intricate designs, unique patterns, and both 2D and 3D logos. You choose from a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and copper, or plastics such as ABS, PEEK, nylon, and polycarbonate. You also select the finish, size, and even add special features like floating pieces or adhesive backs. Here are some common customization options:
- Custom 2D and 3D signs for businesses or events
- Personalized flags, plaques, and gifts
- Monogram initials and wall-mounted logos
- Metal and wood signs with different finishes
- Size adjustments and addition of names or emblems
You preview your layout before production, so you know exactly what you will get. This flexibility lets you create logos that fit your brand and style perfectly.
Efficiency
CNC Logo Cutting makes your production process much more efficient than manual methods. Automated machines reduce the need for hands-on labor, so one skilled operator can manage several machines at once. The process runs continuously, even overnight, which speeds up turnaround times. You save time and money because the machines produce parts with high precision and minimal waste. CAD/CAM software optimizes tool paths, making each cut as fast and accurate as possible. Here is a look at typical production output:
| Contributor | Production Output Estimate | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|
| Contributor A | About 6 sheets per hour (48 per day) | Fast cutting speed |
| Contributor E | 55 sheets per 8-hour day | 6 minutes per sheet at 750 IPM |
| Contributor G | 65+ sheets per day | Speed depends on equipment and part size |
| Contributor R | 70-100 sheets per day | Dual bed router; complex parts take longer per sheet |
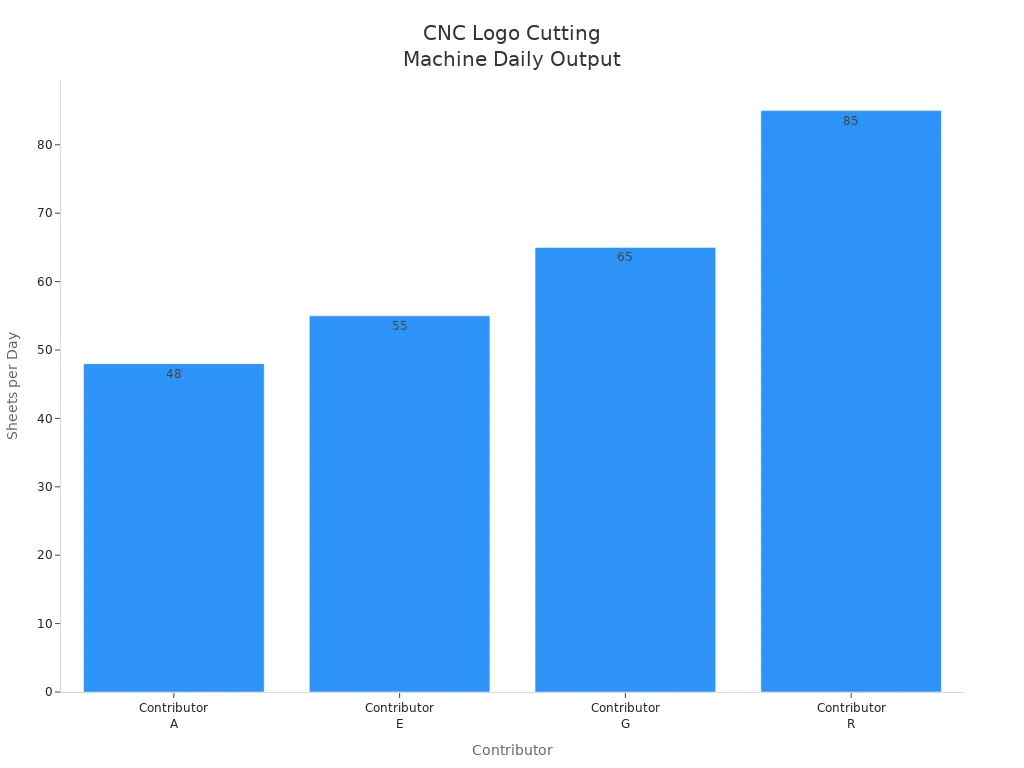
You benefit from faster production, lower costs, and the ability to scale up quickly for large orders. Automated safety features also help protect operators, making the process safer than manual cutting.
CNC Logo Cutting gives you unmatched precision, speed, and flexibility for branding, signage, and custom fabrication. You can create complex, customized designs from materials like acrylic, and metal while minimizing waste and reducing costs. Start your CNC logo cutting at VMT, we ensures consistent results, whether you need a single sign or a large production run.
Frequently Asked Questions About CNC Logo Cutting
What is the main benefit of CNC logo cutting?
You get precise and repeatable results. CNC machines follow your digital design exactly. This process ensures every logo matches your specifications, even for large orders.
What materials can you use for CNC logo cutting?
You can use metals, plastics, and wood. Common choices include aluminum, steel, acrylic, and hardwood. Each material offers different looks and durability for your logo.
What file type do you need for CNC logo cutting?
You need a vector file, such as DXF or STEP. These files give the machine clear paths to follow. Raster images like JPEGs must be converted before use.
What makes CNC logo cutting better than manual methods?
You achieve higher accuracy and faster production. CNC machines reduce human error and handle complex designs with ease. You also save time when you need many identical logos.



