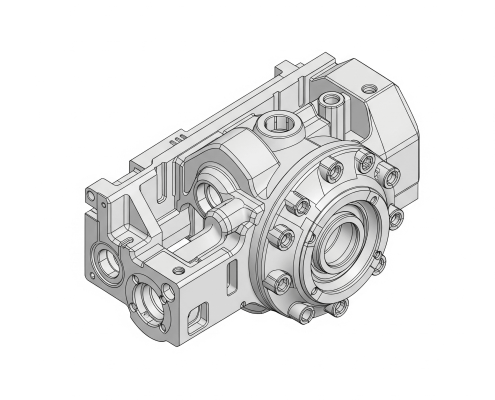
2D vs 3D Drawings: A Guide to the Differences
Are you struggling to fully express complex design details using the limitations of 2d drawing in precision manufacturing? This limitation can lead to miscommunication, increased rework risks, and ultimately impact project timelines and costs. This guide delves into the crucial differences between 2d drawing and 3d engineering drawing, revealing how to choose the best design method for your project needs.
2d drawing provides flat, two-dimensional views of an object, focusing on specific aspects like length and width, ideal for basic schematics. In contrast, 3d engineering drawing offers a multi-dimensional, interactive, and comprehensive representation, allowing for full visualization and analysis of complex geometries, critical for precision manufacturing.
Let’s dive deeper to understand their unique characteristics and applications in detail.
What Is a 2D Drawing?
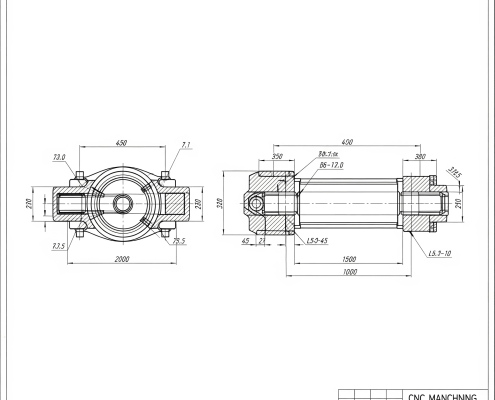
2d drawing, also known as two-dimensional drawings, are flat representations of an object, typically viewed from a single plane.
They convey information using projections like top, front, and side views, along with dimensions and annotations. Common examples include blueprints, architectural plans, and traditional engineering drawings used for manufacturing components.
2D art, like 2D drawings, is created on a flat surface. If you’re wondering whether paper is 2D or 3D, a regular sheet of paper is considered a 2D surface. While effective for simpler parts and conveying basic information, interpreting complex designs from multiple 2 d drawing views can be challenging, often requiring specialized knowledge
At VMT, we have 15 years of CNC machining experience. We know how to read detailed 2D drawings and turn them into precise, high-quality parts.
What is 3D Drawing?
3D drawings, also known as three-dimensional models, show an object in a more realistic way. You can view the model from any angle, zoom in, and rotate it to see all sides. This makes it easier to understand how a part looks, fits, and works.
Compared to 2D drawings, 3D models can include more detailed features. They can show material types and even simulate how parts are put together. This helps spot design problems early, saving time and reducing mistakes.
3D drawings are great for showing complex shapes. You might see 3D drawings of people, cities, or even 3D art drawn on paper. These examples show how flexible and creative 3D drawing can be.
Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Drawings
The choice between a 2d drawing and a 3d engineering drawing is pivotal, directly influencing design, manufacturing, and overall project efficiency in CNC machining. Understanding the difference between 2d and 3d is crucial for making informed decisions. The following is the difference between 2d and 3d drawing:
2D vs 3D Drawing: Representation
A 2d drawing presents a flat, planar view, like a 2d park drawing, requiring multiple views to convey an object’s shape. Conversely, a 3d engineering drawing offers a holistic, volumetric, and multi-dimensional representation, providing a complete spatial understanding.
2D vs 3D Drawing: Clarity & Understanding
While 2d drawing is precise for dimensions, interpreting complex designs often demands specialized knowledge. 3d engineering drawing is far more intuitive, allowing anyone to easily visualize and comprehend the design.
2D vs 3D Drawing: Design Process
The design process with 2d drawing can be linear and sequential; changes in one view often necessitate manual adjustments in others. 3d engineering drawing allows for a dynamic and flexible workflow, where modifications, such as those between a SolidWorks 2d drawing and its corresponding 3d engineering drawing, automatically update across all associated components, speeding up iterations.
2D vs 3D Drawing: Manufacturing Use
2d drawing requires machinists to mentally construct the 3D object, which can introduce interpretation errors. 3d engineering drawing can be directly exported for CAM programming, leading to enhanced accuracy and streamlined production.
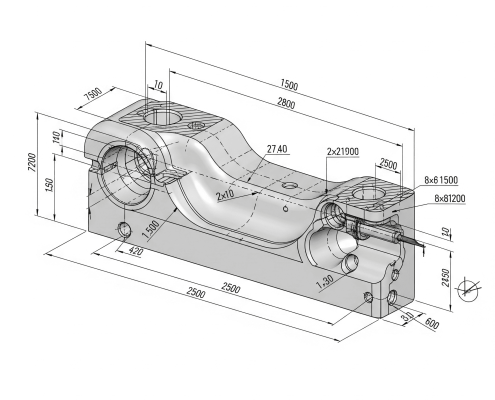
2D vs 3D Drawing: Cost & Time
While the initial software investment for 3d engineering drawing might be higher, it often leads to long-term savings by minimizing design errors and reducing rework. 2d drawing may have lower upfront costs but can incur more expenses in later stages due to potential misinterpretations.
2D vs 3D Drawing: Application Suitability
2d drawing remains suitable for simpler designs, architectural layouts, or conveying specific, isolated details. 3d engineering drawing is indispensable for complex product development and high-precision parts across various industries.
CAD Usage
2d drawing primarily involves drafting in CAD software. The discussion of 2d vs 3d CAD drawings highlights that 3d engineering drawing is essential for advanced modeling, simulation, and direct manufacturing integration.
While some might think 2d and 3d computer graphics are the same, this is a common misconception. The fundamental 2d 3d difference lies in their dimensionality. The difference in 2d and 3d is evident in how they handle complexity. Here’s a summary of the distinctions:
Frequently Asked Questions About 2D and 3D Drawing
What is 2D vs 3D vs 4D drawing?
2D drawings are flat images showing only height and width. 3D drawings add depth, allowing full object views from any angle. 4D drawings include time or motion, showing how a 3D object changes or moves over time, often used in animation, simulation, or construction planning.
What is the Best Software for 2D Drawing?
Popular 2D drawing software includes AutoCAD, DraftSight, and LibreCAD. AutoCAD is widely used for professional engineering and architectural drawings. For beginners or basic needs, LibreCAD is a free and user-friendly option.
How to Convert 2D Drawing into 3D Model?
You can convert a 2D drawing into a 3D model using CAD software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or Fusion 360. Start by importing or tracing the 2D sketch, then use tools like “extrude,” “revolve,” or “loft” to add depth and turn it into a 3D shape.
How to Draw 3D Shapes?
To draw 3D shapes, start with a basic 2D shape like a square or circle. Then add depth by drawing lines extending from the shape and connecting the corners. This forms cubes, cylinders, and other 3D forms. Practice with pencil and paper or try using software like SketchUp.